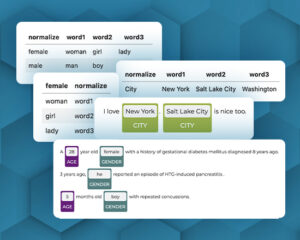
This is the first article of the “Serving Spark NLP via API” series, showcasing how to serve Spark NLP using Synapse ML
Don’t forget to check the other articles in this series, namely:
- How to serve Spark NLP using FastAPI and LightPipelines (Part 2/3), available here.
- How to serve Spark NLP using Databricks Jobs and MLFlow Rest APIs (Part 3/3), available here.
Background
Spark NLP is a Natural Language Understanding Library built on top of Apache Spark, leveranging Spark MLLib pipelines, that allows you to run NLP models at scale, including SOTA Transformers. Therefore, it’s the only production-ready NLP platform that allows you to go from a simple PoC on 1 driver node, to scale to multiple nodes in a cluster, to process big amounts of data, in a matter of minutes.
Before starting, if you want to know more about all the advantages of using Spark NLP (as the ability to work at scale on air-gapped environments, for instance) we recommend you to take a look at the following resources:
- John Snow Labs webpage;
- The official technical documentation of Spark NLP;
- Spark NLP channel on Medium;
- Also, follow Veysel Kocaman, Data Scientist Lead and Head of Spark NLP for Healthcare, for the latest tips.
Motivation
Spark NLP is server-agnostic, what means it does not come with an integrated API server, but offers a lot of options to serve NLP models using Rest APIs.
There is a wide range of possibilities to add a web server and serve Spark NLP pipelines using RestAPI, and in this series of articles we are only describing some of them.
Let’s have an overview of how to use Microsoft’s Synapse ML as an example for that purpose.
Microsoft’s Synapse ML
Synapse ML (previously named SparkMML) is, as they state in their official webpage:
… an ecosystem of tools aimed towards expanding the distributed computing framework Apache Spark in several new directions.
They offer a seamless integratation with OpenCV, LightGBM, Microsoft Cognitive Tool and, the most relevant for our use case, Spark Serving, an extension of Spark Streaming with an integrated server and a Load Balancer, that can attend multiple requests via Rest API, balance and attend them leveraging the capabilities of a Spark Cluster. That means that you can sin up a server and attend requests that will be distributed transparently over a Spark NLP cluster, in a very effortless way.
Strenghts
- Ready-to-use server
- Includes a Load Balancer
- Distributes the work over a Spark Cluster
- Can be used for both Spark NLP and Spark OCR
Weaknesses
- For small use cases that don’t require big cluster processing, other approaches may be faster (as FastAPI using LightPipelines)
- Requires using an external Framework
- This approach does not allow you to customize your endpoints, it uses Synapse ML ones
How to set up Synapse ML to serve Spark NLP pipelines
We will skip here how to install Spark NLP. If you need to do that, please follow this official webpage about how to install Spark NLP or, if Spark NLP for Healthcare if you are using the Healthcare library.
Synapse ML recommends using at least Spark 3.2, so first of all, let’s configure the Spark Session with the required jars packages(both for Synapse ML and Spark) with the the proper Spark version (take a look at the suffix spark-nlp-spark32) and also, very important, add to jars.repository the Maven repository for SynapseML.
sparknlpjsl_jar = "spark-nlp-jsl.jar"
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Spark") \
.master("local[]") \
.config("spark.driver.memory", "16G") \
.config("spark.serializer", "org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer") \
.config("spark.kryoserializer.buffer.max", "2000M") \
.config("spark.jars.packages", "com.microsoft.azure:synapseml_2.12:0.9.5,com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-spark32_2.12:3.4.0")\
.config("spark.jars", sparknlpjsl_jar)\
.config("spark.jars.repositories", "https://mmlspark.azureedge.net/maven")\
.getOrCreate()
After the initialization, add your required imports (Spark NLP) and add to them the SynapseML-specific ones:
import sparknlp
import sparknlp_jsl
...
import synapse.ml
from synapse.ml.io import
Now, let’s create a Spark NLP for Healthcare pipeline to carry out Entity Resolution.
document_assembler = DocumentAssembler()\
.setInputCol("text")\
.setOutputCol("document")
sentenceDetectorDL = SentenceDetectorDLModel.pretrained("sentence_detector_dl_healthcare", "en", 'clinical/models') \
.setInputCols(["document"]) \
.setOutputCol("sentence")
tokenizer = Tokenizer()\
.setInputCols(["sentence"])\
.setOutputCol("token")
word_embeddings = WordEmbeddingsModel.pretrained("embeddings_clinical", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["sentence", "token"])\
.setOutputCol("word_embeddings")
clinical_ner = MedicalNerModel.pretrained("ner_clinical", "en", "clinical/models") \
.setInputCols(["sentence", "token", "word_embeddings"]) \
.setOutputCol("ner")
ner_converter_icd = NerConverterInternal() \
.setInputCols(["sentence", "token", "ner"]) \
.setOutputCol("ner_chunk")\
.setWhiteList(['PROBLEM'])\
.setPreservePosition(False)
c2doc = Chunk2Doc()\
.setInputCols("ner_chunk")\
.setOutputCol("ner_chunk_doc")
sbert_embedder = BertSentenceEmbeddings.pretrained('sbiobert_base_cased_mli', 'en','clinical/models')\
.setInputCols(["ner_chunk_doc"])\
.setOutputCol("sentence_embeddings")\
.setCaseSensitive(False)
icd_resolver = SentenceEntityResolverModel.pretrained("sbiobertresolve_icd10cm_augmented_billable_hcc","en", "clinical/models") \
.setInputCols(["ner_chunk", "sentence_embeddings"]) \
.setOutputCol("icd10cm_code")\
.setDistanceFunction("EUCLIDEAN")
resolver_pipeline = Pipeline(
stages = [
document_assembler,
sentenceDetectorDL,
tokenizer,
word_embeddings,
clinical_ner,
ner_converter_icd,
c2doc,
sbert_embedder,
icd_resolver
])
Let’s use a clinical note to test Synapse ML.
clinical_note = """A 28-year-old female with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosed eight years prior to presentation and subsequent type two diabetes mellitus (T2DM), one prior episode of HTG-induced pancreatitis three years prior to presentation, associated with an acute hepatitis, and obesity with a body mass index (BMI) of 33.5 kg/m2, presented with a one-week history of polyuria, polydipsia, poor appetite, and vomiting. Two weeks prior to presentation, she was treated with a five-day course of amoxicillin for a respiratory tract infection. She was on metformin, glipizide, and dapagliflozin for T2DM and atorvastatin and gemfibrozil for HTG. She had been on dapagliflozin for six months at the time of presentation. Physical examination on presentation was significant for dry oral mucosa; significantly, her abdominal examination was benign with no tenderness, guarding, or rigidity."""
Since SynapseML serves a RestAPI, we will be sending JSON requests. Let’s define a simple json with the clinical note:
data_json = {"text": clinical_note }
Now, let’s spin up a server using Synapse ML Spark Serving. It will consist of:
- a streaming server that will receive a json and transform it into a Spark Dataframe
- a call to Spark NLP transform on the dataframe, using the pipeline
- a write operation returning the output also in json format.
#1: Creating the streaming server and transforming json to Spark Dataframe
serving_input = spark.readStream.server() \
.address("localhost", 9999, "benchmark_api") \
.option("name", "benchmark_api") \
.load() \
.parseRequest("benchmark_api", data.schema)
#2: Applying transform to the dataframe using our Spark NLP pipeline
serving_output = resolver_p_model.transform(serving_input) \
.makeReply("icd10cm_code")
#3: Returning the response in json format
server = serving_output.writeStream \
.server() \
.replyTo("benchmark_api") \
.queryName("benchmark_query") \
.option("checkpointLocation", "file:///tmp/checkpoints-{}".format(uuid.uuid1())) \
.start()
And we are ready to test the endpoint using the requests library.
import requests
res = requests.post("http://localhost:9999/benchmark_api", data= json.dumps(data_json))
And last, but not least, let’s check the results:
for i in range (0, len(response_list.json())):
print(response_list.json()[i]['result'])
Results (list of ICD-10-CM codes from NER chunks)
O2441 O2411 P702 K8520 B159 E669 Z6841 R35 R631 R630 R111...
Do you want to know more?
- Check the example notebooks in the Spark NLP Workshop repository, available here
- Visit John Snow Labs and Spark NLP Technical Documentation websites
- Follow us on Medium: Spark NLP and Veysel Kocaman
- Write to for any additional request you may have