In this article, I give a brief introduction to Randomized Controlled Trials (RCT). Also, an overview of the classification models and pretrained pipelines available in Spark NLP for the classification of RCT.
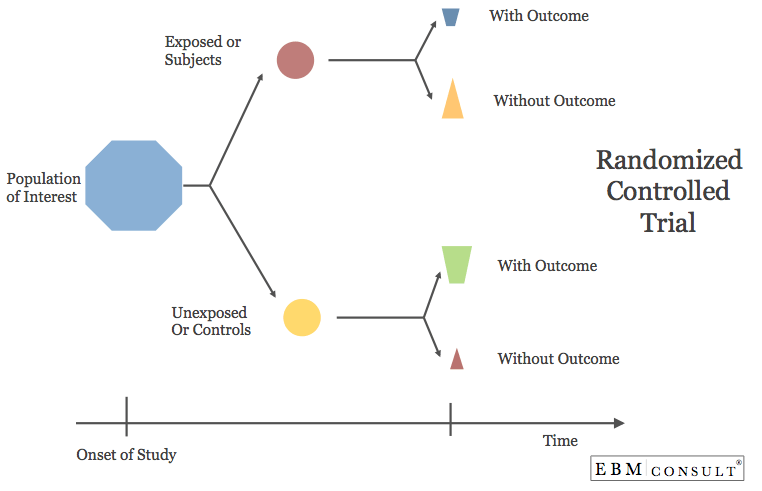
What are Randomized controlled trials (RCT)?
An RCT is a type of study in which participants are randomly assigned to one of two or more clinical interventions or treatments. The RCT is the most scientifically rigorous method of hypothesis testing available, and is regarded as the gold standard trial for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions.
In clinical research, randomized controlled trials (RCT) are the best way to study the safety and efficacy of new treatments. RCT are used to answer patient-related questions and are required by governmental regulatory bodies as the basis for approval decisions.
Why are RCT important?
Because the techniques utilised during the execution of an RCT minimise the potential of confounding factors influencing the outcomes, it is thought to provide the most credible data on the effectiveness of treatments. As a result, the results of RCT are more likely to be closer to the genuine effect than the results of other study methodologies.
Why is it difficult to identify the RCT articles?
The term “RCT” is frequently absent or applied inconsistently in controlled vocabularies of major research databases. As a result, people conducting systematic reviews must often manually read (“screen”) thousands of irrelevant records in order to locate a small number of RCT that are relevant. This is one of the reasons why doing systematic reviews is time-consuming and costly, an issue made worse by the rapid development of the published evidence base.
What have we achieved?
We give SOTA models that can determine whether or not a scientific publication is an RCT. Furthermore, we have pre-trained pipelines that are already fitted with certain annotators and transformers based on the use case and can be launched with only one line of code.
What type of dataset have we used?
We utilised a classification dataset to see if the model could identify whether or not a scientific paper was an RCT (True or False).

1. Classification using UniversalSentenceEncoder
The Universal Sentence Encoder encodes text into high-dimensional vectors that can be used for text classification, semantic similarity, clustering and other natural language tasks.
The model is trained and optimized for greater-than-word length text, such as sentences, phrases or short paragraphs. It is trained on a variety of data sources and a variety of tasks with the aim of dynamically accommodating a wide variety of natural language understanding tasks. The input is the variable-length English text and the output is a 512-dimensional vector. We apply this model to the STS benchmark for semantic similarity. The universal-sentence-encoder model has trained with a deep averaging network (DAN) encoder.
For further information regarding USE, visit the models hub page: https://nlp.johnsnowlabs.com/2020/04/17/tfhub_use.html
Now let’s look at the code and understand the components inside the pipeline:
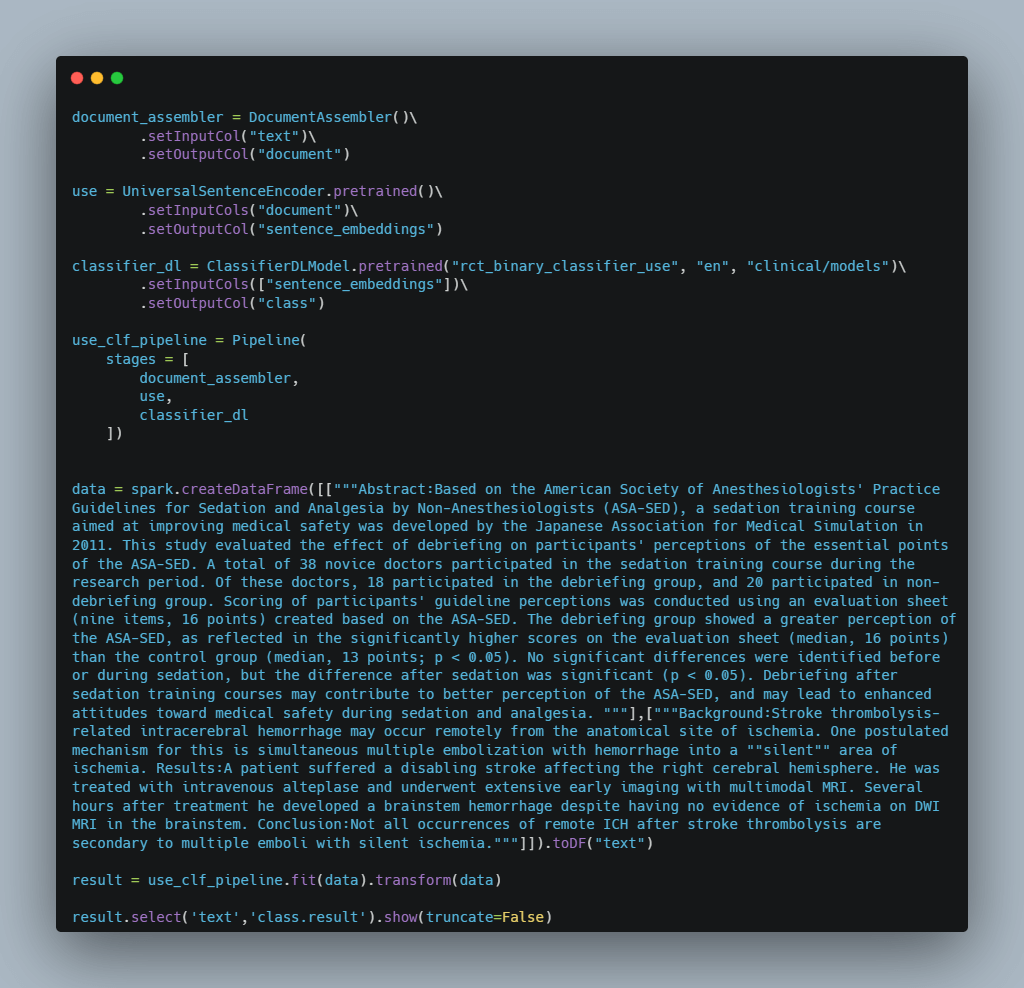
Let Us Break It Down:
- In Spark NLP, DocumentAssembler is a crucial transformer that serves as an initial entry point to Spark NLP for any Spark data frame.
- Then, we have the UniversalSentenceEncoder which we have earlier discussed.
- After that, we have used ClassifierDLModel.
ClassifierDLModelis the very first multi-class text classifier in Spark NLP and it uses various text embeddings as an input for text classifications. TheClassifierDLModelannotator uses a deep learning model (DNNs) that is built inside TensorFlow and supports up to 100 classes. ClassifierDLModel uses the state-of-the-art Universal Sentence Encoder as an input for text classifications. - Now, We build the Spark NLP pipeline by specifying its components like DocumentAssembler, UniversalSentenceEncoder and ClassifierDLModel.
- Then, with text as the column, we specify our data and generate our Spark data frame. This text column will be supplied to DocumentAssembler, our good friend.After that, using our spark data frame, we .fit() on the pipeline (df). This is where our transformers and the spark data frame meet.
Finally, we obtain the output shown below!
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
|text |result |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
|Abstract:Based on the American Society of Anesthesiologists' Practice Guidelines for Sedation and Analgesia by Non-Anesthesiologists (ASA-SED), a sedation training course aimed at improving medical safety was developed by the Japanese Association for Medical Simulation in 2011. This study evaluated the effect of debriefing on participants' perceptions of the essential points of the ASA-SED. A total of 38 novice doctors participated in the sedation training course during the research period. Of these doctors, 18 participated in the debriefing group, and 20 participated in non-debriefing group. Scoring of participants' guideline perceptions was conducted using an evaluation sheet (nine items, 16 points) created based on the ASA-SED. The debriefing group showed a greater perception of the ASA-SED, as reflected in the significantly higher scores on the evaluation sheet (median, 16 points) than the control group (median, 13 points; p < 0.05). No significant differences were identified before or during sedation, but the difference after sedation was significant (p < 0.05). Debriefing after sedation training courses may contribute to better perception of the ASA-SED, and may lead to enhanced attitudes toward medical safety during sedation and analgesia. |[true] |
|Background:Stroke thrombolysis-related intracerebral hemorrhage may occur remotely from the anatomical site of ischemia. One postulated mechanism for this is simultaneous multiple embolization with hemorrhage into a ""silent"" area of ischemia. Results:A patient suffered a disabling stroke affecting the right cerebral hemisphere. He was treated with intravenous alteplase and underwent extensive early imaging with multimodal MRI. Several hours after treatment he developed a brainstem hemorrhage despite having no evidence of ischemia on DWI MRI in the brainstem. Conclusion:Not all occurrences of remote ICH after stroke thrombolysis are secondary to multiple emboli with silent ischemia. |[false]|
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
2. Classification using BertSentenceEmbeddings
This model contains pre-trained weights of BioBERT, a language representation model for the biomedical domain, especially designed for biomedical text mining tasks such as biomedical named entity recognition, relation extraction, question answering, etc. The details are described in the paper “BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining”
For more information about this model, visit the models hub page: https://nlp.johnsnowlabs.com/2020/09/19/sent_biobert_pubmed_base_cased.html
BertSentenceEmbeddings can provide higher accuracy than UniversalSentenceEncoder. Although, when compared to USE, training may take longer.
Let’s look at the pipeline of BertSentenceEmbeddings based RCT classifier model.
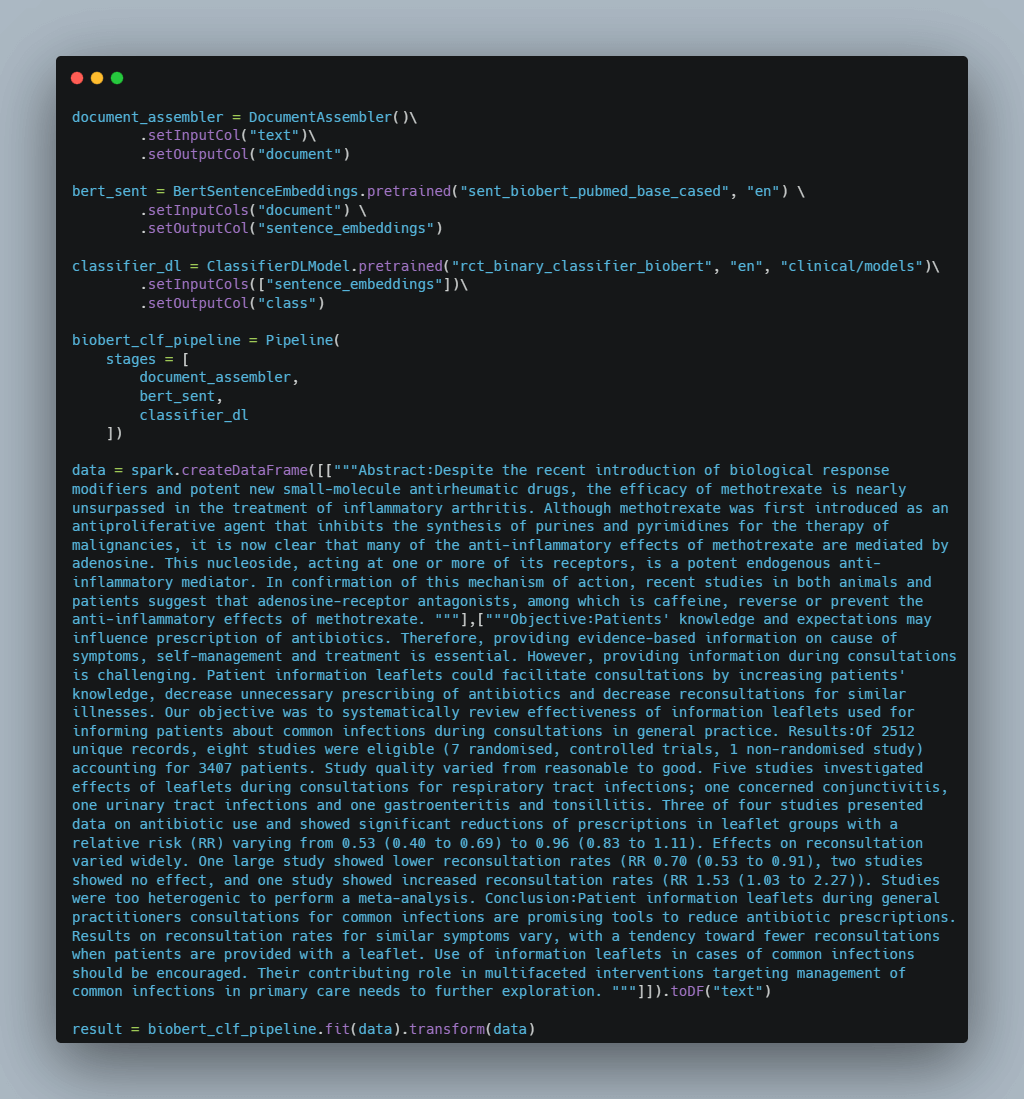
Now, let’s look at the results of this model.
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
|text |result |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
|Abstract:Despite the recent introduction of biological response modifiers and potent new small-molecule antirheumatic drugs, the efficacy of methotrexate is nearly unsurpassed in the treatment of inflammatory arthritis. Although methotrexate was first introduced as an antiproliferative agent that inhibits the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines for the therapy of malignancies, it is now clear that many of the anti-inflammatory effects of methotrexate are mediated by adenosine. This nucleoside, acting at one or more of its receptors, is a potent endogenous anti-inflammatory mediator. In confirmation of this mechanism of action, recent studies in both animals and patients suggest that adenosine-receptor antagonists, among which is caffeine, reverse or prevent the anti-inflammatory effects of methotrexate. |[false]|
|Objective:Patients' knowledge and expectations may influence prescription of antibiotics. Therefore, providing evidence-based information on cause of symptoms, self-management and treatment is essential. However, providing information during consultations is challenging. Patient information leaflets could facilitate consultations by increasing patients' knowledge, decrease unnecessary prescribing of antibiotics and decrease reconsultations for similar illnesses. Our objective was to systematically review effectiveness of information leaflets used for informing patients about common infections during consultations in general practice. Results:Of 2512 unique records, eight studies were eligible (7 randomised, controlled trials, 1 non-randomised study) accounting for 3407 patients. Study quality varied from reasonable to good. Five studies investigated effects of leaflets during consultations for respiratory tract infections; one concerned conjunctivitis, one urinary tract infections and one gastroenteritis and tonsillitis. Three of four studies presented data on antibiotic use and showed significant reductions of prescriptions in leaflet groups with a relative risk (RR) varying from 0.53 (0.40 to 0.69) to 0.96 (0.83 to 1.11). Effects on reconsultation varied widely. One large study showed lower reconsultation rates (RR 0.70 (0.53 to 0.91), two studies showed no effect, and one study showed increased reconsultation rates (RR 1.53 (1.03 to 2.27)). Studies were too heterogenic to perform a meta-analysis. Conclusion:Patient information leaflets during general practitioners consultations for common infections are promising tools to reduce antibiotic prescriptions. Results on reconsultation rates for similar symptoms vary, with a tendency toward fewer reconsultations when patients are provided with a leaflet. Use of information leaflets in cases of common infections should be encouraged. Their contributing role in multifaceted interventions targeting management of common infections in primary care needs to further exploration. |[true] |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
3. Classification using MedicalBertForSequenceClassification
MedicalBertForSequenceClassification can load BERT Models with sequence classification/regression head on top (a linear layer on top of the pooled output) e.g. for multi-class document classification tasks.
Let’s look at the pipeline:
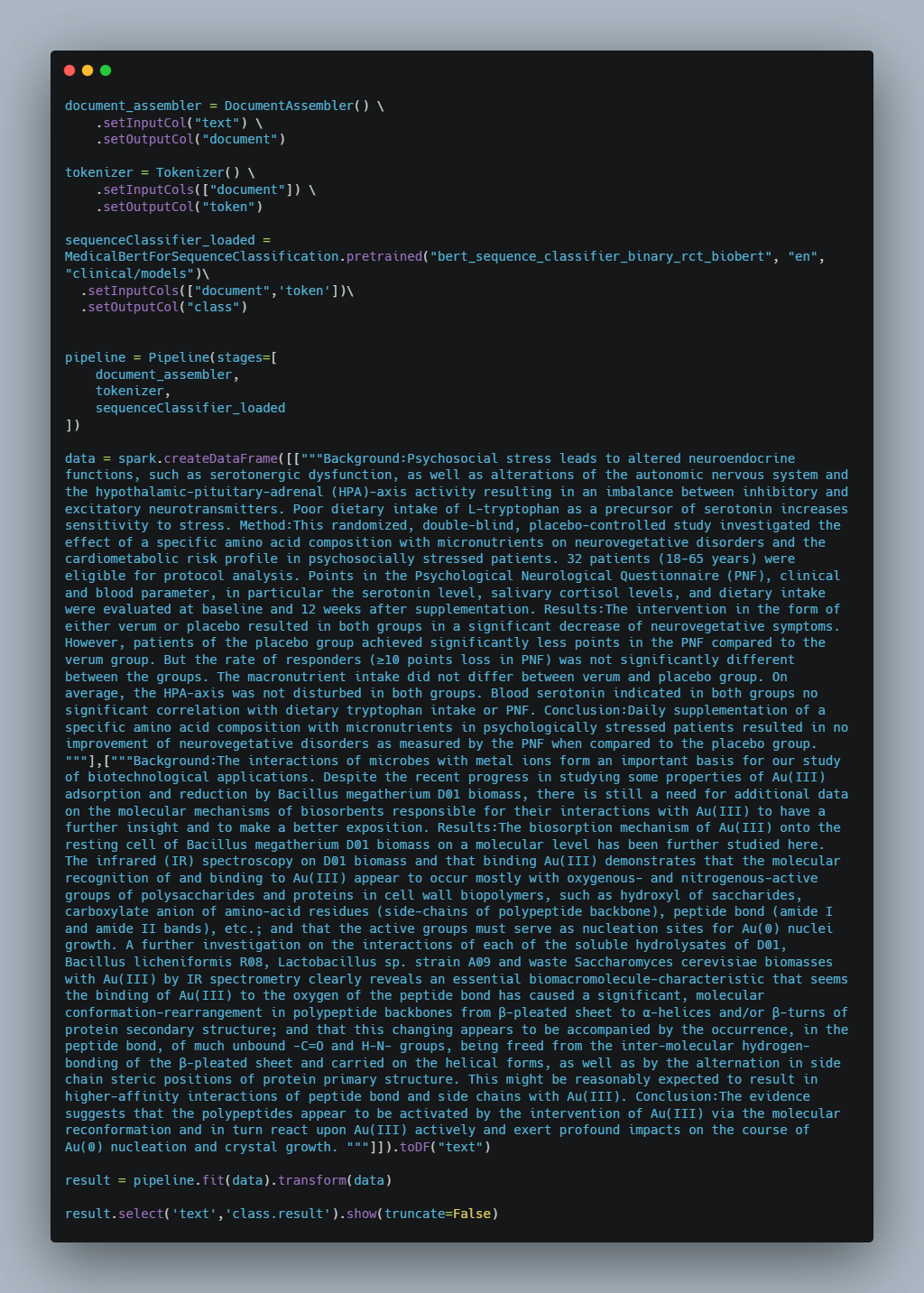
We get the following output:
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
|text |result |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
|Background:Psychosocial stress leads to altered neuroendocrine functions, such as serotonergic dysfunction, as well as alterations of the autonomic nervous system and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA)-axis activity resulting in an imbalance between inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters. Poor dietary intake of L-tryptophan as a precursor of serotonin increases sensitivity to stress. Method:This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study investigated the effect of a specific amino acid composition with micronutrients on neurovegetative disorders and the cardiometabolic risk profile in psychosocially stressed patients. 32 patients (18-65 years) were eligible for protocol analysis. Points in the Psychological Neurological Questionnaire (PNF), clinical and blood parameter, in particular the serotonin level, salivary cortisol levels, and dietary intake were evaluated at baseline and 12 weeks after supplementation. Results:The intervention in the form of either verum or placebo resulted in both groups in a significant decrease of neurovegetative symptoms. However, patients of the placebo group achieved significantly less points in the PNF compared to the verum group. But the rate of responders (≥10 points loss in PNF) was not significantly different between the groups. The macronutrient intake did not differ between verum and placebo group. On average, the HPA-axis was not disturbed in both groups. Blood serotonin indicated in both groups no significant correlation with dietary tryptophan intake or PNF. Conclusion:Daily supplementation of a specific amino acid composition with micronutrients in psychologically stressed patients resulted in no improvement of neurovegetative disorders as measured by the PNF when compared to the placebo group. |[True] |
|Background:The interactions of microbes with metal ions form an important basis for our study of biotechnological applications. Despite the recent progress in studying some properties of Au(III) adsorption and reduction by Bacillus megatherium D01 biomass, there is still a need for additional data on the molecular mechanisms of biosorbents responsible for their interactions with Au(III) to have a further insight and to make a better exposition. Results:The biosorption mechanism of Au(III) onto the resting cell of Bacillus megatherium D01 biomass on a molecular level has been further studied here. The infrared (IR) spectroscopy on D01 biomass and that binding Au(III) demonstrates that the molecular recognition of and binding to Au(III) appear to occur mostly with oxygenous- and nitrogenous-active groups of polysaccharides and proteins in cell wall biopolymers, such as hydroxyl of saccharides, carboxylate anion of amino-acid residues (side-chains of polypeptide backbone), peptide bond (amide I and amide II bands), etc.; and that the active groups must serve as nucleation sites for Au(0) nuclei growth. A further investigation on the interactions of each of the soluble hydrolysates of D01, Bacillus licheniformis R08, Lactobacillus sp. strain A09 and waste Saccharomyces cerevisiae biomasses with Au(III) by IR spectrometry clearly reveals an essential biomacromolecule-characteristic that seems the binding of Au(III) to the oxygen of the peptide bond has caused a significant, molecular conformation-rearrangement in polypeptide backbones from β-pleated sheet to α-helices and/or β-turns of protein secondary structure; and that this changing appears to be accompanied by the occurrence, in the peptide bond, of much unbound -C=O and H-N- groups, being freed from the inter-molecular hydrogen-bonding of the β-pleated sheet and carried on the helical forms, as well as by the alternation in side chain steric positions of protein primary structure. This might be reasonably expected to result in higher-affinity interactions of peptide bond and side chains with Au(III). Conclusion:The evidence suggests that the polypeptides appear to be activated by the intervention of Au(III) via the molecular reconformation and in turn react upon Au(III) actively and exert profound impacts on the course of Au(0) nucleation and crystal growth. |[False]|
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
The training period for MBFSC is longer than for earlier models, but the accuracy makes it worthwhile.
RCT Classification Pretrained Pipelines
Spark NLP provides pre-trained pipelines that are already equipped with certain annotators and transformers according to various use cases, which saves you the time of having to build a pipeline from start.
Let’s take a look at the code
Now, let’s look at the results of this model.
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------+
| text | rct |
|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------|
| """Abstract:Based on the American Society of Anesthesiologists' Practice Guidelines for Sedation and Analgesia by Non-Anesthesiologists (ASA-SED), a sedation training course aimed at improving medical safety was developed by the Japanese Association for Medical Simulation in 2011. This study evaluated the effect of debriefing on participants' perceptions of the essential points of the ASA-SED. A total of 38 novice doctors participated in the sedation training course during the research period. Of these doctors, 18 participated in the debriefing group, and 20 participated in non-debriefing group. Scoring of participants' guideline perceptions was conducted using an evaluation sheet (nine items, 16 points) created based on the ASA-SED. The debriefing group showed a greater perception of the ASA-SED, as reflected in the significantly higher scores on the evaluation sheet (median, 16 points) than the control group (median, 13 points; p < 0.05). No significant differences were identified before or during sedation, but the difference after sedation was significant (p < 0.05). Debriefing after sedation training courses may contribute to better perception of the ASA-SED, and may lead to enhanced attitudes toward medical safety during sedation and analgesia. """ | true |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------+
We can see that it’s only a one-liner, and we can retrieve the results, which makes it really simple to utilise.
Conclusion
For the time being, that’s all I have to say. The difficulties of finding RCT papers have been discussed in this post, as well as how we have made it easier to classify the articles using pre-trained models and pipelines.
SparkNLP Resources
- Spark NLP documentation and Quick Start Guide
- Introduction to Spark NLP: Foundations and Basic Components
- Introduction to Spark NLP: Installation and Getting Started
- Spark NLP 101: Document Assembler
- Spark NLP 101: LightPipeline
- Text Classification in Spark NLP
- Named Entity Recognition (NER) using BERT in Spark NLP




























