As expected, most of the readers who will be attracted to this blog will be of either data science or healthcare background. Those working in the data science field might not realize all the dimensions of the importance of the social determinants of health and what efforts are done to just develop an evidence-based framework for SDoH. On the other side, those working in the healthcare field, might not realize what is NLP. Most healthcare professionals believe that NLP stands only for Neural Linguistic Programming per se!
This is why the first part of this blog will give an introductory brief about Natural Language Processing (NLP), while the second half will try to summarize the efforts done related to SDoH.
What is an NLP Model?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the art and science that aims to understand, interpret, and analyze human language (speech and text for different languages (English, Spanish, French, etc.)) using artificial intelligence techniques.
NLP can be applied to perform different tasks (translation, summarization, named-entity recognition, relationship extraction, speech recognition, topic segmentation, etc.) in dirrefent areas (medical NLP, legal NLP, etc.)
What are the Components of the NLP Model?
There are 5 main components of the NLP model:
-
Morphological and Lexical Analysis
Identifying and analyzing the structure of words and expressions. Lexicon means the collection of words and phrases in a language. Lexical analysis is dividing a text into paragraphs, words, and sentences. Single words are broken down into their components, while other non-word tokens (e.g.: punctuations) are separated from the words.
-
Syntactic Analysis
In the NLP world, the word is the smallest unit of syntax.
The syntax can be defined as the principles and rules that determined the sentence structure for any language.
Words’ order is considered the top priority for syntax analysis. Words’ order can markedly affect the meaning.
Following the grammatical rules of the sentence can help in successful syntactic analysis.
The words are parsed into the structure to represent the relationship between the words.
-
Semantic Analysis
It is responsible for parsing linear sequences of words into structures. It also reveals the actual association between different words. The semantic Analysis role is dependent on the outcome of the syntactic analyzer which assigns meanings.
Semantics in general is concerned mainly with the literal meaning of words, phrases, and sentences. It only extracts the real meant meaning from the given context.
-
Discourse Integration
It is concerned with detecting and directing the sense of the context towards the right meaning. It depends on the meaning of the same sentence in addition to the successor sentence.
-
Pragmatic Analysis
This component is concerned with the social and outside word knowledge content and its reflection on the sentence interpretation. In other words, it can be defined as selecting the correct choice of language suitable or matching a certain situation.
Recognizing cooperative dialogs and their effect can be realized by applying a set of specific rules. For example, the phrase “put on the facemask?” should be understood as a request, not as an imperative phrase.
Transfer Learning Enabled through Pre-trained Models
In the NLP world, Transfer Learning means to train a model on one dataset and then adapt that model to perform different NLP functions (spell-checkers, search keywords auto-complete features, topic classification, intent detection, extracting ketwords from a text, …etc.) on a different dataset.
This methodology can benefit those who are beginners in the field of NLP or who do not have time to build models from scratch on their own.
Pre-trained models are not 100% accurate, but it saves time and effort. Training datasets and pre-trained models have been explained in a previous blog.
By understanding what NLP is and what is an NLP pre-trained model, we can realize the importance of applying the same concepts in business or health.
The second part of the blog will focus mainly on the Social Determinants of Health (SDoH).
How Can We Define the Social Determinants of Health (SDoH)?
Before exploring the definition of SDoH we should understand the definition of 2 other terms, namely “Health Disparity” and “Health Inequities “.
Health Disparity is concerned with the comparison between two groups about a load of illness, injury, disability, or mortality. On the other hand, if we referred to “Healthcare Disparity”, we should be referring to the comparison between the two groups with regards to access to care, insurance, and quality of service.
Another important definition to understand before proceeding further is “Health Inequities”. Health inequities refer to the comparison between the differences in health status and/or resource distribution between different population groups. Those differences could be due to the variation in the circumstances in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. It could be also due to incorrect and unfair governmental policies. Simply, due to the variation in the social determinants of health.
Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) or sometimes referred to as (SDH) are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age that could have an effect and shape the health of the community. Such determinants are so intermingled and complex.
They may include factors like socioeconomic status, education, neighborhood, and physical environment, employment, and social support networks, as well as access to health care, that are responsible for most health inequities. They are shaped by the distribution of power and wealth at the global or the local levels.
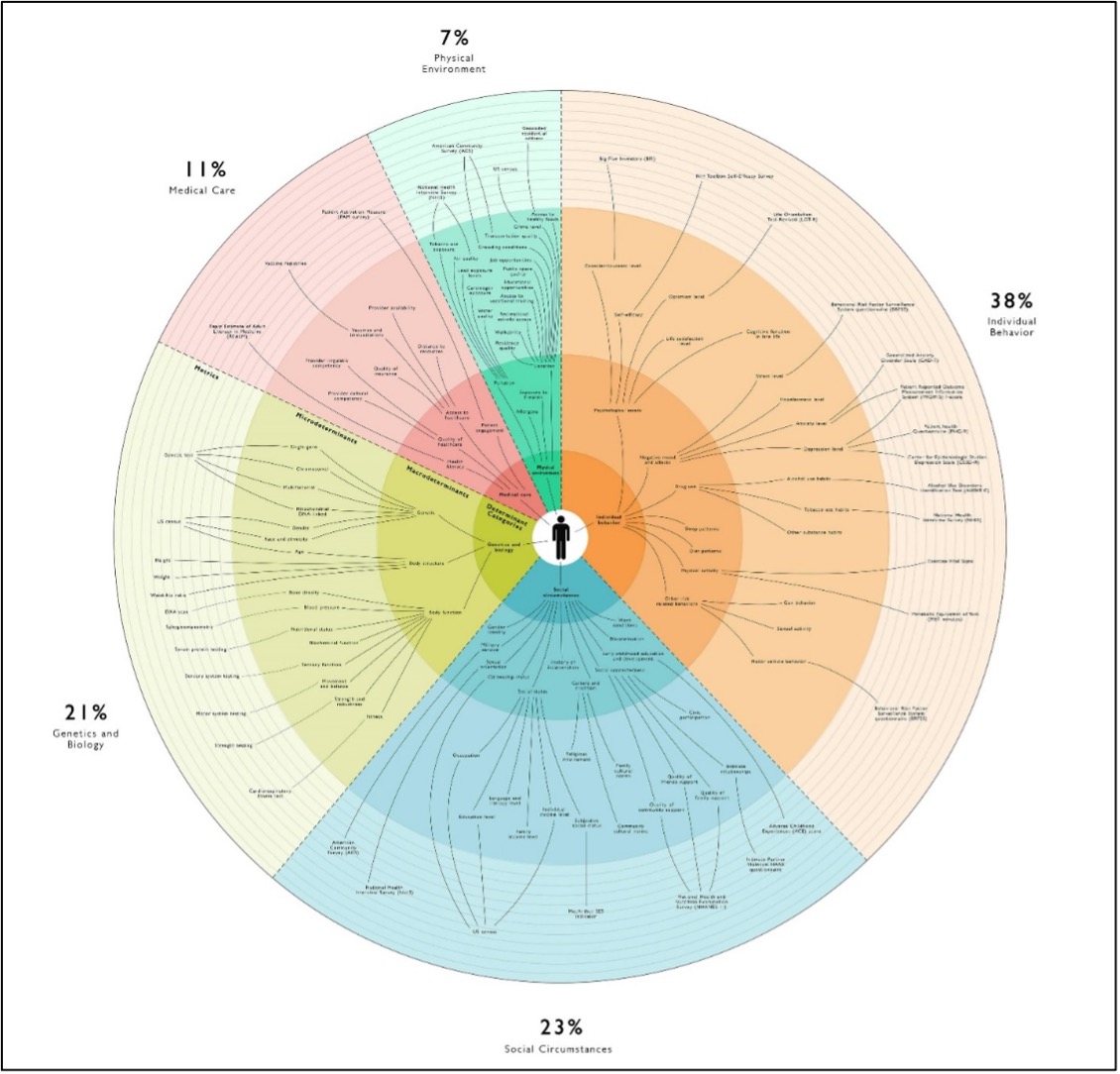
Figure 1: Social Determinants of Health
The importance of Social Determinants of Health
Studying the social determinants of health is critical for enhancing the quality of health and mitigating the disparities in health and healthcare.
Factors affecting SDoH can be within the scope of the healthcare system or outside it. It could be related to other sectors (e.g.: agricultural or industrial) and still have its effect on healthcare equity.
Payment systems vary worldwide and even within the US where there are different payment models (federal state initiatives, Medicaid, and Medicare-specific initiatives).
Hundreds of studies were done to indicate the importance and activities done related to SDoH or what features could be linked to getting out the maximum benefit from the SDoH.
Analyzing social needs is critical to care plan providers. In 2017, by analyzing the social needs, we realized that 19 states required Medicaid-managed care plans to screen for and/or provide referrals for social needs.
In another study, analyzing Medicaid managed care plans revealed that (91%) of the responding plans were concerned with SDoH.
There is a distinct research study [1] described an innovative process for determining SDoH by geocoding and linking Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems with Community Information Systems (CIS). This methodology was successful in addressing health inequities and disparities.
Moreover, different SDoH studies were used to develop a holistic framework to reduce inequities in HIV, Viral Hepatitis, Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs), and TB. [2]
The importance of integrating SDoH in governmental public policies was very prominent in a Botswana case study published by the WHO. Many areas covered appeared to have a great effect on health equity in Botswana. Some of those factors were:
– Early childhood development and education.
– Healthy housing and shelters
– Provision of water
– Healthy environment
– Urbanization/human settlements/rural development
– Fair employment and decent work
– Social protection across the life course
Botswana and other case studies led to the development of the “Health in All Policies” concept.
The health in all policies concept makes decision-makers follow a certain decision-making procedure where interactions and mutual effects between health sectors and other sectors are studied and analyzed before the final policy setting or any decision making.
SDoH-related Efforts and Activities in the US
In the US, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has a long list of projects and activities in a trial to get out the maximum benefits from the SDoH information available.
Different CDC programs were concerned with housing, education, and transportation. Most of the efforts were done in collaboration with communities. Here are some of the CDC projects that addressed the SDoH:
1- Built Environment and Health Initiative: Designing and Building Healthy Places:
This project is concerned with improving public health through improving community design. Moreover, studying the linkage between both through many research studies.
2- Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Program:
This program is concerned with childhood lead poisoning and other housing-related health hazards.
3- The National Program to Eliminate Diabetes-Related Disparities in Vulnerable Populations:
This program is concerned with social, cultural, economic, and environmental factors affecting health disparities associated with diabetes.
4- Partnerships to Improve Community Health (PICH):
This program is concerned with improving community health by reducing the prevalence of the chronic disease. This is done by partnerships with school districts, hospitals, community centers, and public health offices.
5- Racial and Ethnic Approaches to Community Health (REACH):
This program is concerned with reducing racial and ethnic disparities in health.
6- State Level Implementation of the Essentials for Childhood Framework:
This program aims to implement a framework that aids the children to grow up in a healthy environment.
7- STRYVE: Striving To Reduce Youth Violence Everywhere:
This program targets preventing youth violence before it starts through studying, analyzing, and providing suitable education, laws, and community planning.
8- Health Impact in 5 Years (HI-5):
This is one of the most important projects for the CDC. It focuses on community-wide approaches for improving population health by simply focusing on SDoH.
The Health Impact in 5 Years (HI-5) is concerned with positive health impacts, results within five years, and cost-effectiveness.
The Office of Disease Prevention and Health Prevention (ODPHP) has established an important project called Healthy People 2020. The project aims to retain high-quality, longer life expectancy with guaranteed improved health care. Besides, it aims to achieve health equity and eliminate disparities among all groups.
Related Datasets
The reader can find relevant datasets on some CDC or WHO-related websites, but I think the most precious thing the reader can take out from this blog is the Social Determinants Of Health Data Package which the John Snow Labs catalog offers.
This data package contains 7 important datasets for those interested in the SDoH:
- Daily Smoking Prevalence
- Disability Weights
- HIV Incidence Prevalence and Mortality
- ICD-9 And ICD-10 Codes Mapped to Fatal Nonfatal Causes
- Opioid Overdose Mortality in the US
- Population Estimates 1970-2017
- Socio-Demographic Index Values
All the datasets are curated both manually and automatically by a specialized team of data scientists and NLP experts. The majority of the team has healthcare domain experience and educational background. 80% of them have an MSc degree, 36% have Ph.D. or MD degrees. The team shows high diversity; they can speak up to 22 different languages.
Besides the value of having such a data package, you will gain the knowledge of how to build a successful team and make the successful merge between healthcare sciences and data sciences, especially NLP.
References
[1] Comer KF, Grannis S, Dixon BE, Bodenhamer DJ, Wiehe SE. Incorporating geospatial capacity within clinical data systems to address social determinants of health. Public Health Rep. 2011;126(SUPPL. 3):54–61.
[2] Hepatitis V. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Establishing a Holistic Framework to Reduce Inequities in HIV, Viral Hepatitis, STDs, and Tuberculosis in the United States. Atlanta (GA): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Contro. Cdc [Internet]. 2010; Available from: www.cdc.gov/socialdeterminants