The NLP Tools feature is a new addition to the Medical Chatbot, providing specialized capabilities for processing medical texts through Natural Language Processing (NLP). This feature allows users to access five distinct state-of-the-art accuracy tools, each designed for specific tasks related to medical data handling and analysis.
Healthcare Tools
- Deidentification/Obfuscation of PHI: Automatically detects and masks or obfuscates protected health information (PHI) from medical text to ensure privacy and compliance with data protection regulations. Users can specify to de-identify or obfuscate the medical text based on their requirements.
- General Medical Entity Extraction: Identifies and extracts general medical entities from text, facilitating quick access to relevant medical terms and concepts.
- Oncological Entity Extraction: Specialized for recognizing and extracting terms related to oncology, aiding in the analysis of cancer-related medical texts.
- Posology Entity Extraction: Focuses on extracting dosage and medication instructions from medical documents, which is crucial for understanding treatment protocols.
Customizable Accessibility
- Users can enable or disable NLP tools based on their specific needs or preferences, allowing for a personalized experience and control over the processing features used.
Accessing Tools
- NLP tools can be invoked in two ways: via regular queries in natural language or by using the ‘@’ operator for direct tool activation.
- Typing ‘@’ at the beginning of the query box triggers a contextual menu displaying all available tools, similar to tagging functionality in Microsoft Teams.
- The @ operator also allows direct access to
MedResearchandWikipediatools for targeted questions. For instance, when using@medical_researchat the beginning of your question, the chatbot will directly engage theMedResearchtool without requiring the user to select from multiple options, ensuring a streamlined interaction for focused research tasks. - Similarly, for Wikipedia and NLP Tools, each tool can be easily selected and utilized with the @ operator as follows:
@search_wikipedia: Query Wikipedia Pages@deidentification: De-identification of Medical Text@obfuscation: Obfuscation of Medical Text@ner_medical: General Medical Entity Extraction@ner_medical_oncology: Oncological Entity Extraction@ner_medical_posology: Posology Entity Extraction
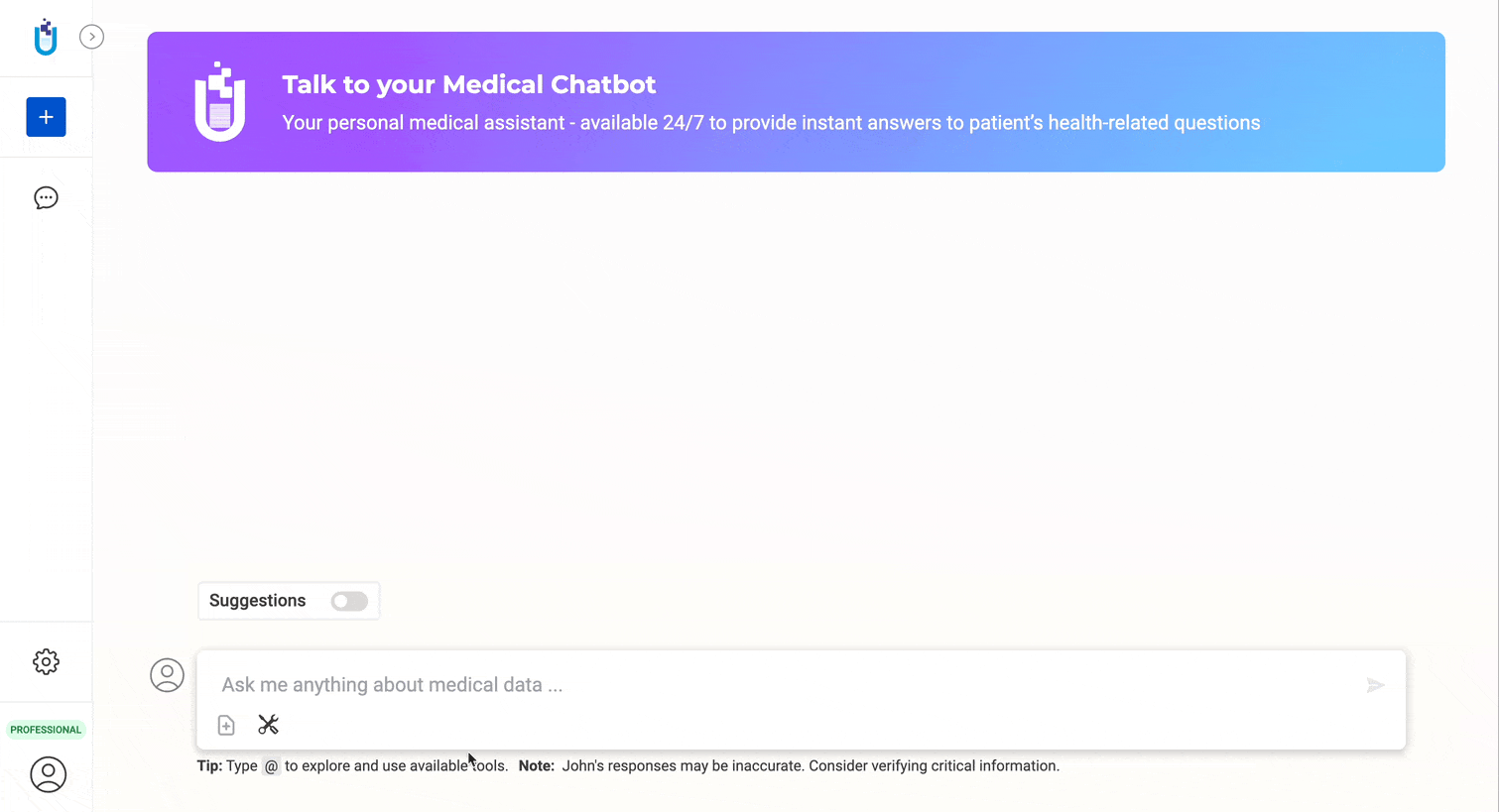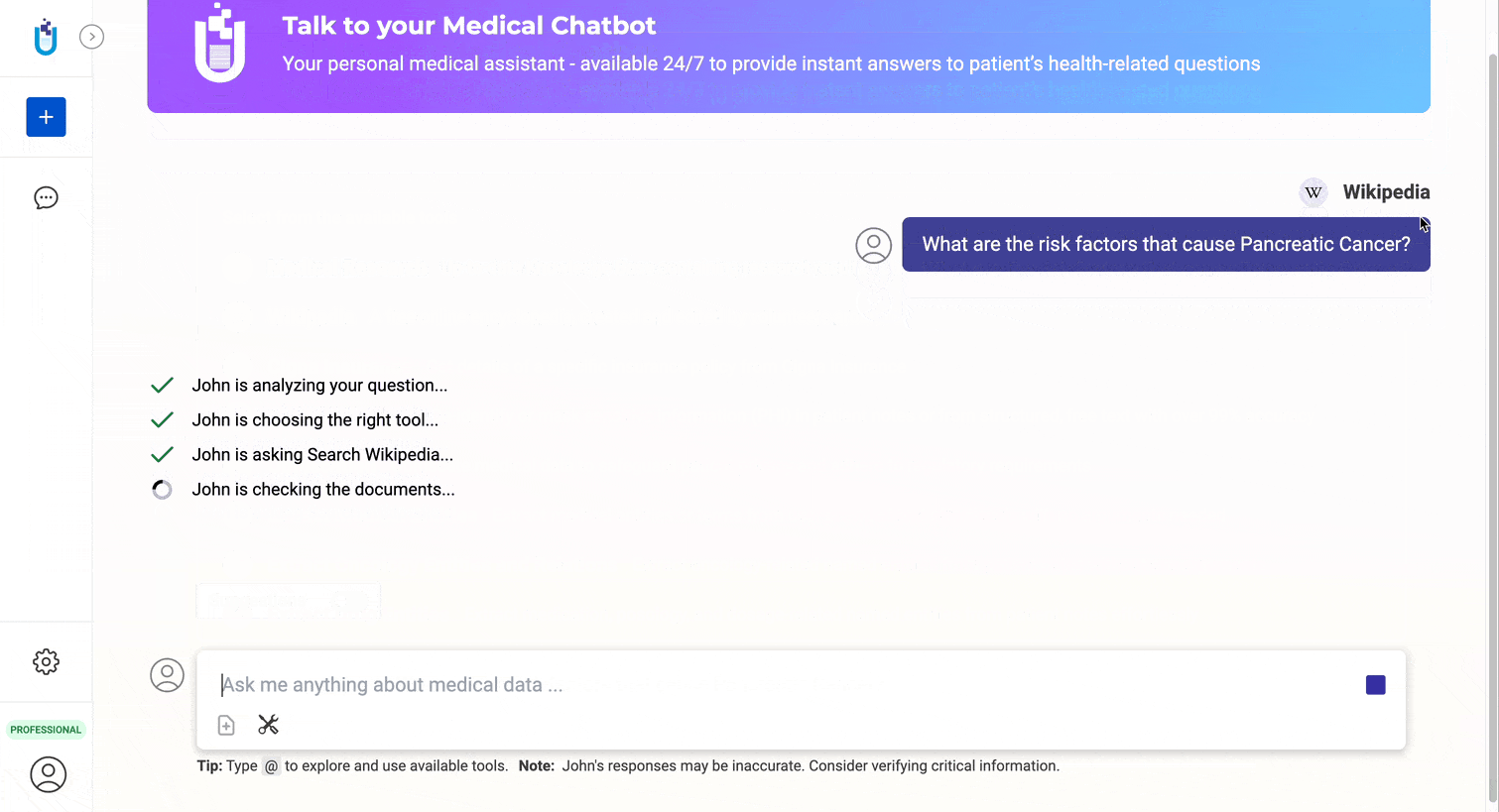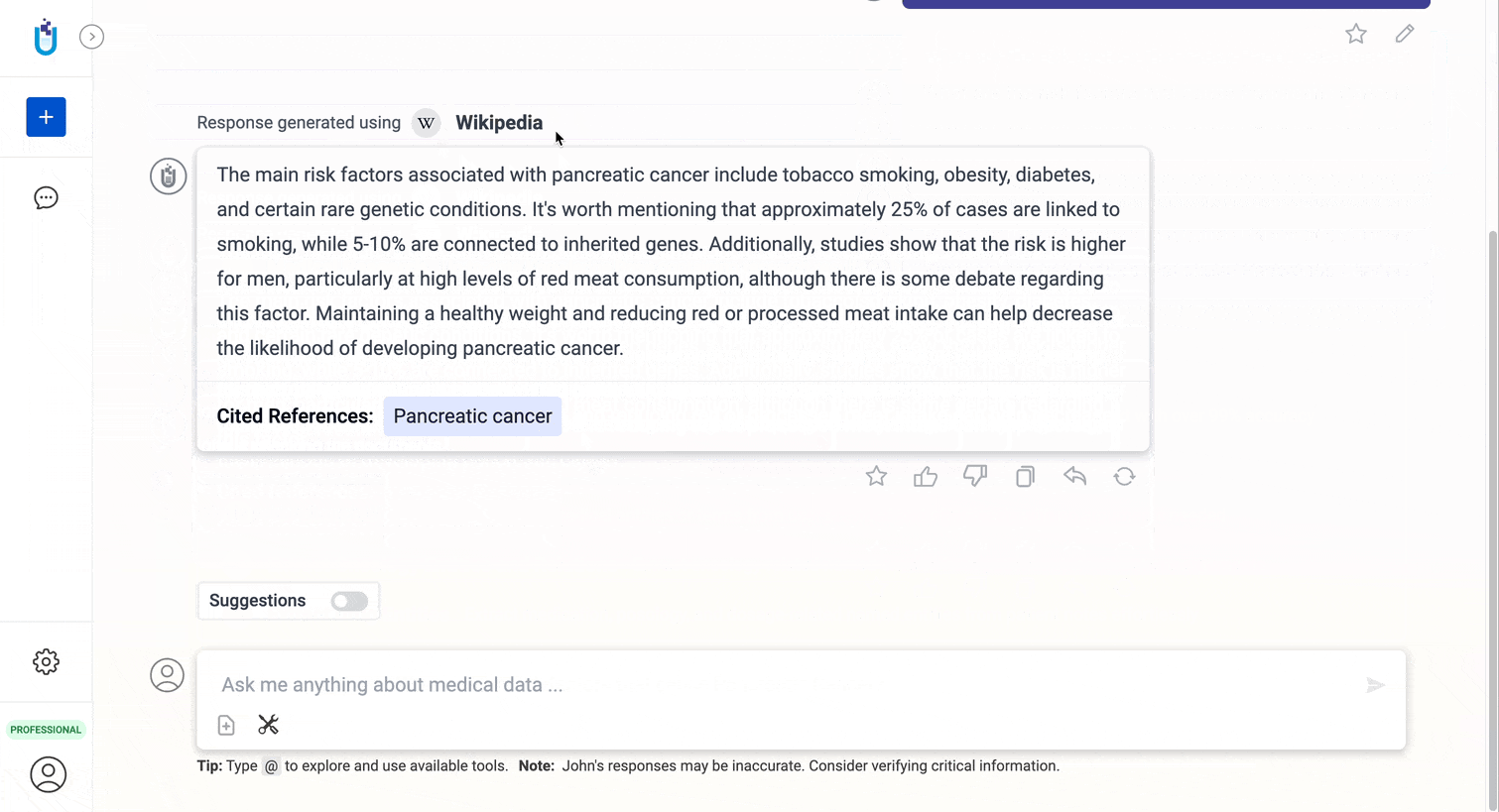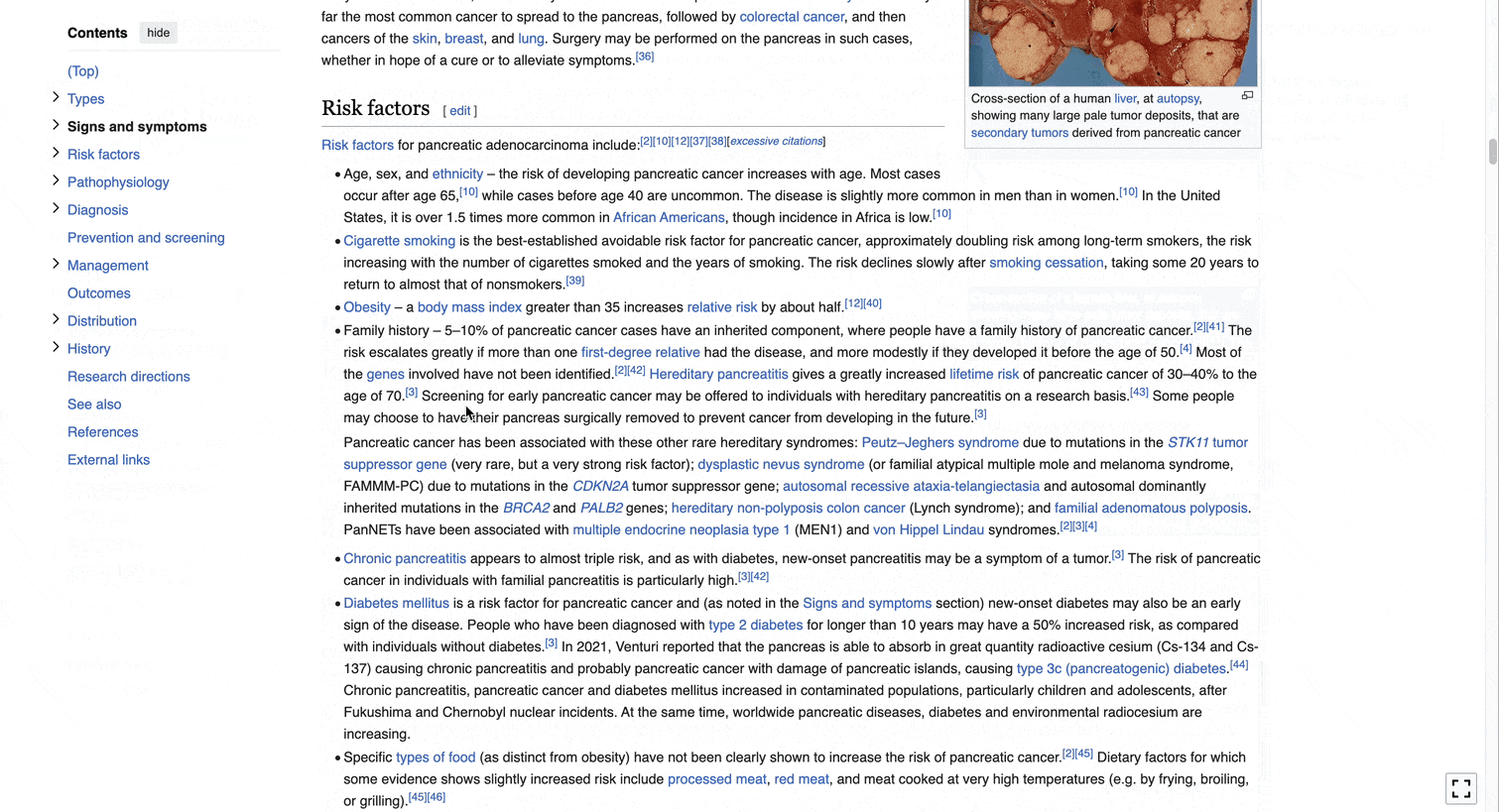
- When interacting with the chatbot, the generated answer prominently displays the tool used for response generation right above the answer itself. This clarification ensures users know which tool was utilized.
- Similarly, when selecting a specific tool using the ‘@’ Selector in your query, the chosen tool is labeled at the top of the query, making it clear which tool was requested for the response generation.
- Hence, users can better understand the specialties of these tools and experiment to obtain the best possible responses according to their needs.
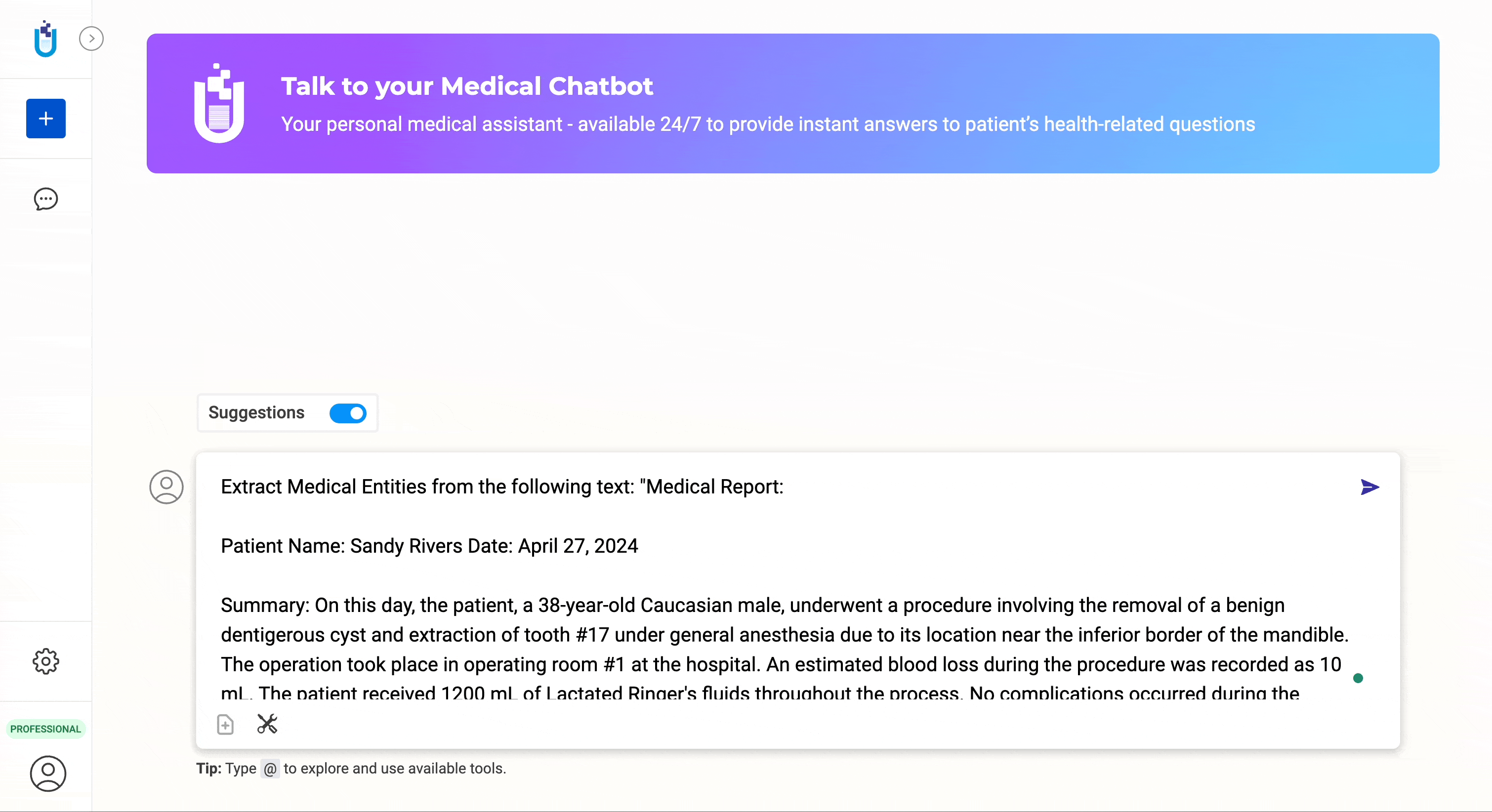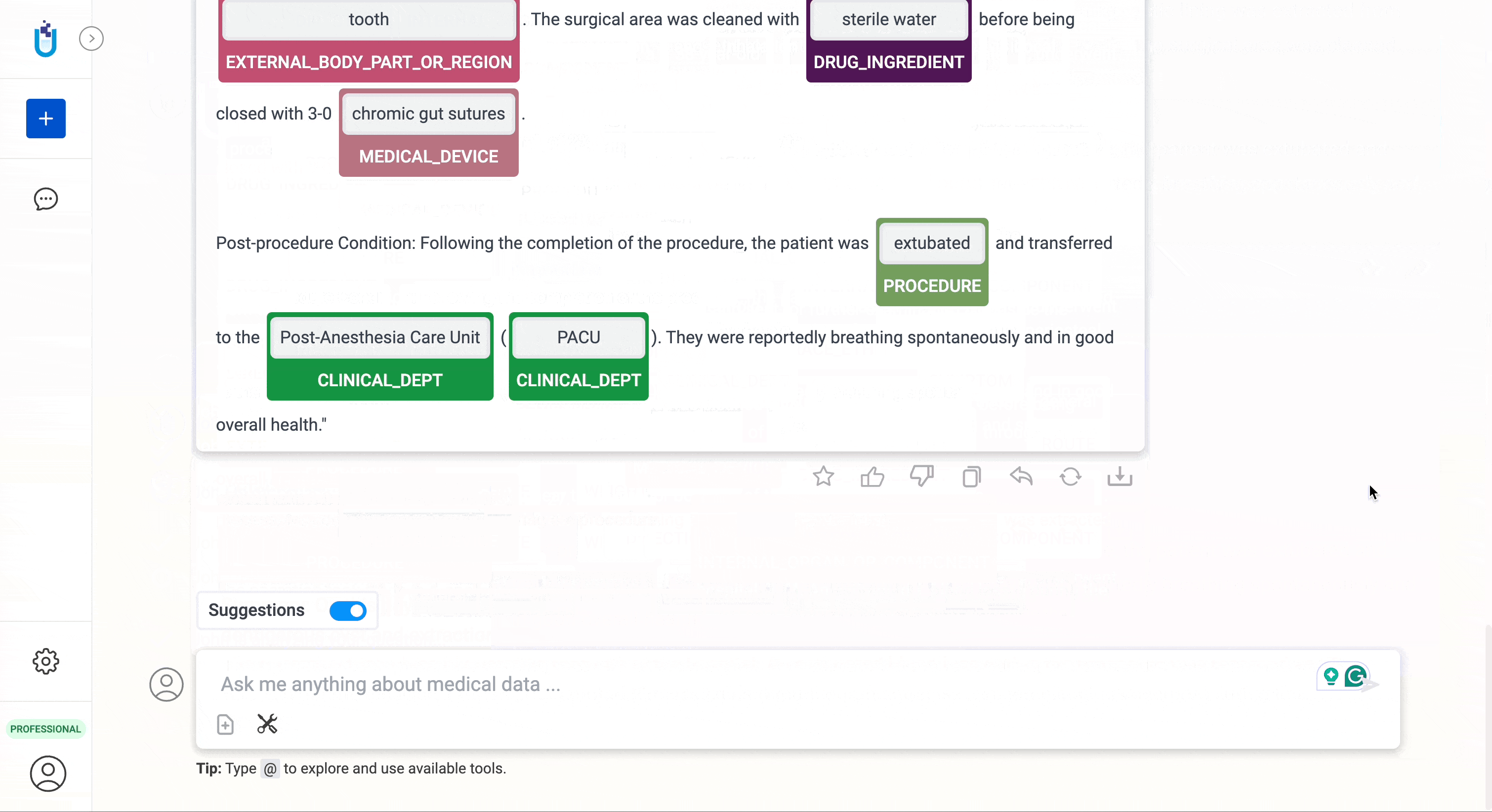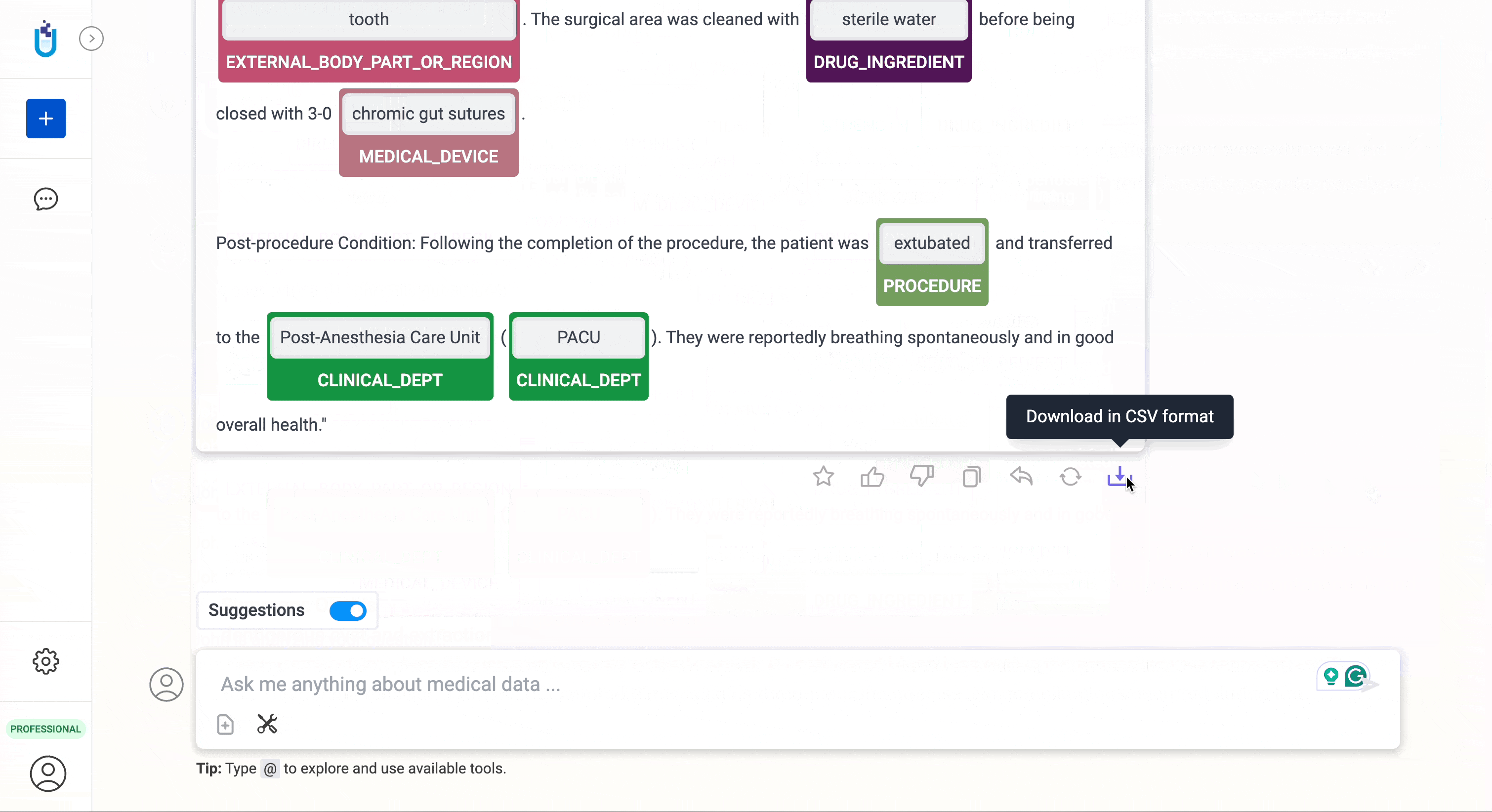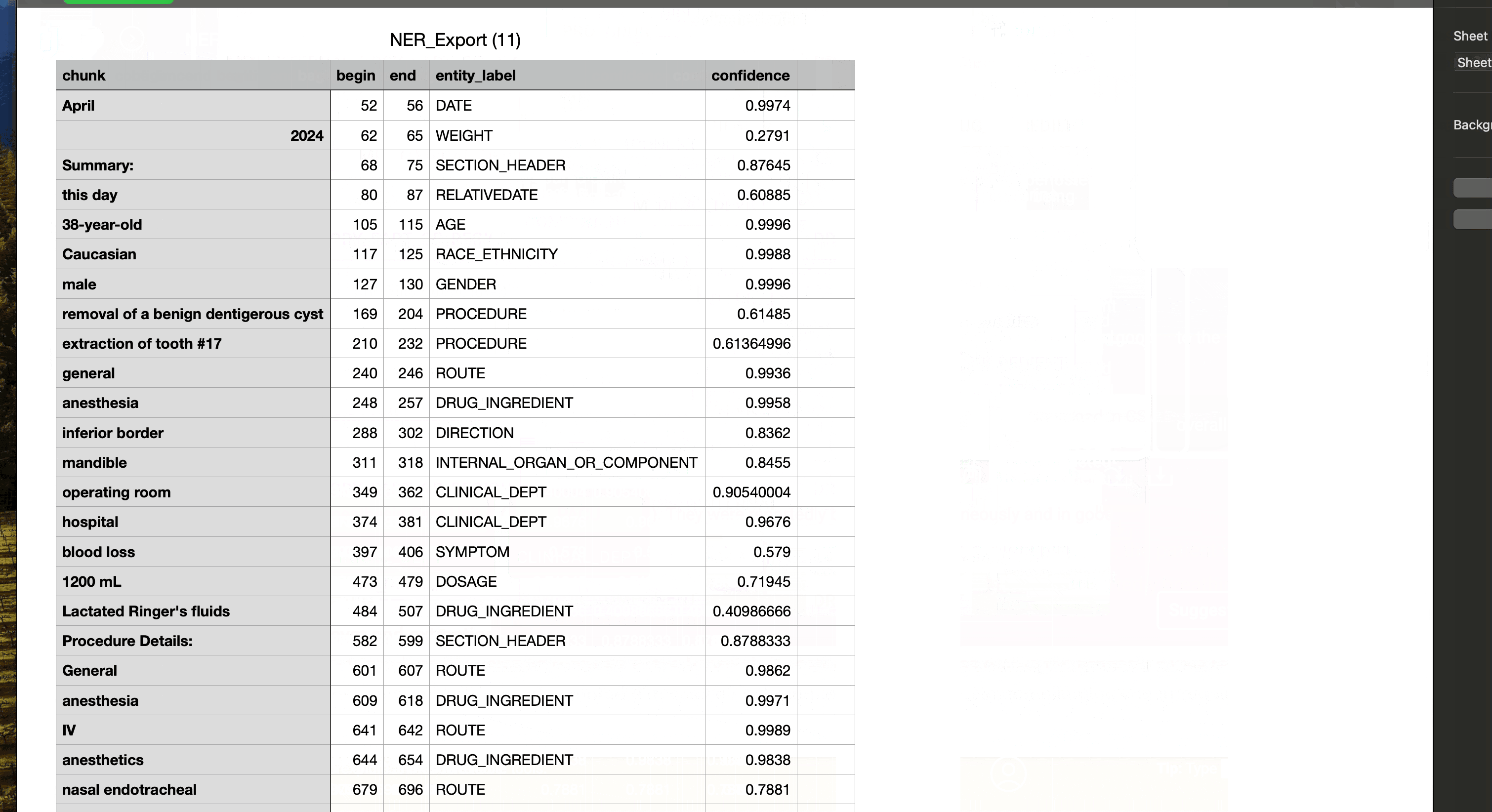
Export results in CSV format
- All the Entity Extraction results computed using the NLP tools can be exported in CSV format. For each detected entity, the export also contains confidence information, ensuring transparency and reliability in data analysis.
User Benefits
- Enhanced Privacy and Compliance: Safeguards sensitive information by efficiently deidentifying PHI from medical texts.
- Focused Content Extraction: Enables precise extraction of medical entities tailored to general, oncological, and posology contexts, enhancing the utility and accuracy of information retrieval.
- User-Controlled Flexibility: Offers the flexibility to tailor tool engagement to individual preferences and requirements.
- Efficient Tool Access: Simplifies the process of accessing specific NLP tools through intuitive user interface mechanisms.
Getting Started
To get started, simply click here to create a new account or sign up using your LinkedIn profile. Begin exploring the Medical Chatbot today and receive evidence-based responses, complete with cited sources, drawn from our extensive and daily-updated medical knowledge database.