Exploring the Innovators and Challengers in the Commercial LLM Landscape beyond OpenAI: Anthropic, Cohere, Mosaic ML, Cerebras, Aleph Alpha, AI21 Labs and John Snow Labs.
This blog post explores the emerging players in the commercial large language model (LLM) landscape, namely Anthropic, Cohere, Mosaic ML, Cerebras, Aleph Alpha, AI21 Labs and John Snow Labs. While OpenAI is well-known, these companies bring fresh ideas and tools to the LLM world. We discuss their unique offerings, compliance with the EU AI Act, pricing, and performance on various tasks. To dive deeper into the topic, read our guide to large language models.
In the burgeoning world of artificial intelligence, large language models (LLMs) are the new vanguard, shaping how we interact with machines and expanding the boundaries of what technology can achieve. As the field evolves, a dynamic set of companies have emerged, each contributing unique perspectives and solutions to the landscape. They range from established tech giants flexing their AI muscles, to innovative start-ups pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
This landscape is a vibrant blend of commercial entities and open-source advocates, with a wealth of diversity in their origin stories, funding, and the models they have developed. From licensed models delivered via APIs to open-source alternatives available for local deployment, the offerings span a broad spectrum, meeting the varied needs of developers, businesses, and researchers worldwide.
In this blog post, we will dive into the fascinating ecosystem of LLM companies. We’ll start with an overview, presenting a snapshot of the current landscape. We’ll then delve into more detailed profiles of each major player, exploring their unique contributions, the models they’ve brought to life, and the strategic decisions that have shaped their paths. So, whether you’re an AI enthusiast, a developer navigating the LLM waters, or just a curious mind, join us as we journey through the bustling landscape of LLM companies.
The landscape of large language models (LLMs) companies
The landscape of large language models (LLMs) companies is diverse, featuring both well-established organizations and dynamic newcomers. Dominating the industry are leading LLM companies, such as OpenAI, which was founded in 2015 and has accumulated $11.3 billion in funding by June 2023. Known for their GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 (ChatGPT) models, OpenAI provides access to these tools through a licensed API.
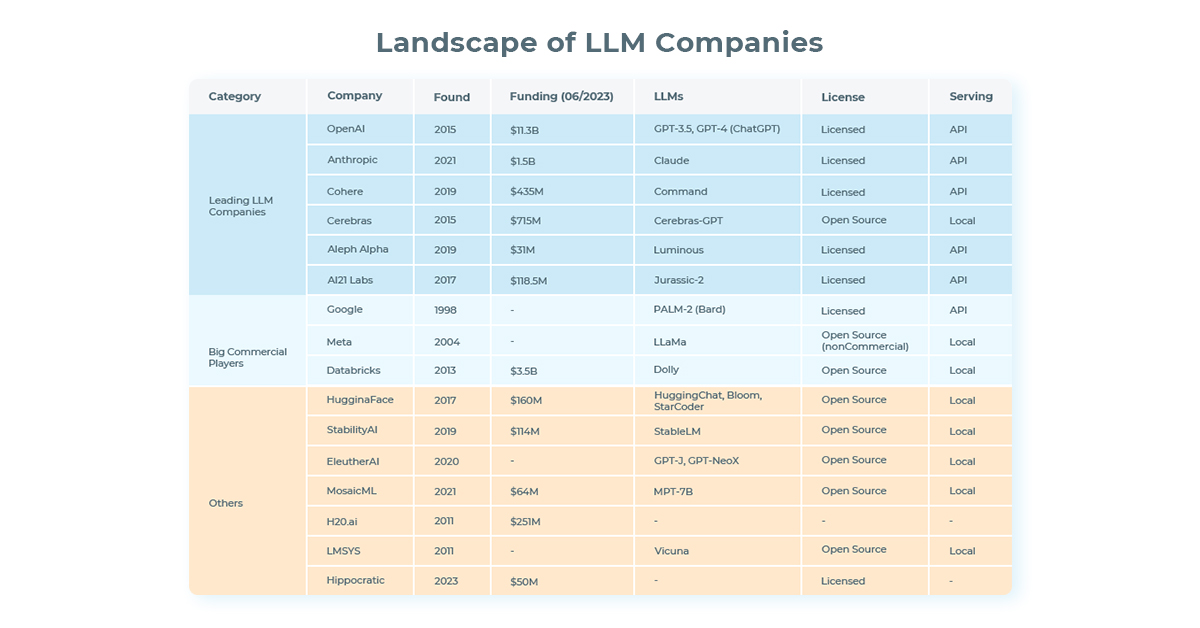
snapshot of the major players in the LLM industry as of June 2023, illustrating their diverse origins, funding levels, models, licensing approaches, and deployment methods (image by author).
Other leading players in the sector include Anthropic, Cohere, and AI21 Labs, all of which offer LLMs through licensed APIs. Anthropic, the youngest among these firms, was established in 2021 and has managed to raise $1.5 billion in funding, using it to develop their model named Claude. Similarly, Cohere, founded in 2019 with $435 million in funding, offers the model named Command.
A unique player among the leaders is Cerebras, not only known for its open-source model, Cerebras-GPT, which operates locally, but also for its state-of-the-art supercomputer designed to train LLMs at a remarkable scale. Also, Aleph Alpha, despite relatively modest funding of $31 million, has made significant strides with its Luminous model.
Big commercial players such as Google, Meta, and Databricks also have a presence in the LLM market. Google’s PALM-2 (Bard) and Meta’s LLaMA models stand out, with the latter available as open-source for non-commercial uses. Databricks, with $3.5 billion in funding, offers Dolly, an open-source model operating locally.
The field of LLMs also includes a range of smaller players that have made notable contributions. HuggingFace, with $160 million in funding, has developed HuggingChat, Bloom, and StarCoder. StabilityAI, with its $114 million funding, offers the StableLM model, and EleutherAI has brought forth GPT-J and GPT-NeoX. MosaicML, LMSYS, and the newly founded Hippocratic also play integral roles in this thriving market.
Overall, the landscape of LLM companies is complex and full of potential, with many entities playing different roles. These companies have collectively fostered a competitive environment, which will undoubtedly drive more innovation in the field of AI and LLMs in the future.
Beyond the Big Names: New Endeavors Revolutionizing LLMs
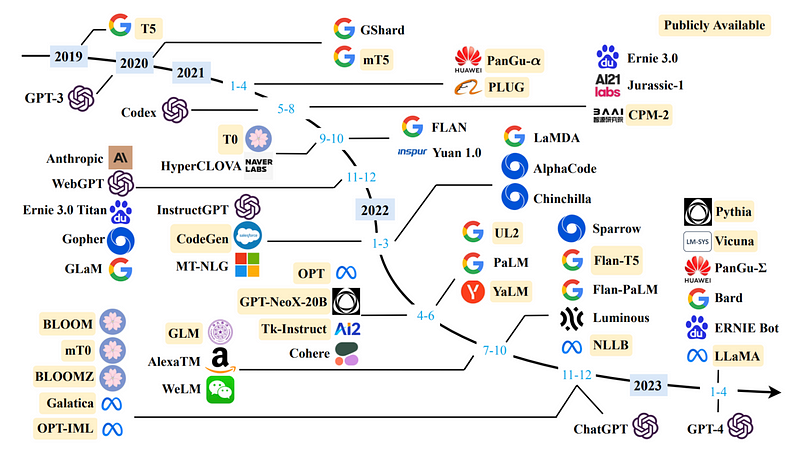
In addition to the major players outlined in our landscape of LLM companies, there are numerous open-source efforts that contribute significantly to the field. These projects often serve specific niches or aim to address certain limitations within the industry, thus playing an essential role in shaping the broader AI landscape.
Notable among these in healthcare domain is the MedAlpaca, MedVicuna, ChatDoctor, and Clinical Camel suite of models that are exemplary of the focused efforts being made to leverage LLMs in this life-critical industry. The value of these models becomes evident when considering the numerous challenges the healthcare sector faces. From the increasing complexity of medical information and documentation to the need for personalized patient care, the healthcare industry is ripe for AI intervention.
An intriguing open-source project is OpenAssistant by LAION. This German non-profit offers a chat-based assistant capable of understanding tasks, interacting with third-party systems, and retrieving information dynamically. This level of functionality points towards a future where AI isn’t just a tool, but a dynamic assistant capable of a wide range of operations.
Similarly, Falcon, a model by the Technology Innovation Institute in Abu Dhabi, has quickly ascended to prominence. Released under the Apache 2.0 license, Falcon topped the Open LLM leaderboard swiftly and has emerged as one of the most interesting foundational models in the space.
Berkeley Labs’ BAIR has contributed to the open-source scene with Koala, a version of LLaMA fine-tuned on dialogue data scraped from the web and various public datasets. This includes high-quality responses from other large language models, question-answering datasets, and human feedback datasets, showcasing the potential of combinatorial model training.
GPT4ALL is another interesting endeavour that democratizes LLM usage. This project provides a free-to-use, locally running, privacy-aware chatbot, requiring neither a GPU nor an internet connection. This kind of innovation opens up the possibility of using sophisticated language models on consumer-grade CPUs, increasing accessibility.
Finally, OpenLLaMA, a public preview of a permissively licensed open-source reproduction of Meta AI’s LLaMA, has been trained on the RedPajama dataset. This initiative reflects the larger trend of reproducing proprietary models in the open-source sphere, thus promoting greater transparency and accessibility.
The variety of these efforts reflects the vast potential and adaptability of LLMs. From medical applications to dialogue systems, and from foundational models to privacy-aware healthcare chatbots, the breadth of open-source projects underscores the vibrancy of the LLM landscape and hints at the exciting developments yet to come.
Beyond OpenAI in LLM Landscape
In this comprehensive exploration of the landscape of large language model (LLM) companies, we will delve into the innovative offerings and advancements brought forth by Anthropic, Cohere, Cerebras, Aleph Alpha, and AI21 Labs. While OpenAI, a prominent player in the field, will not be covered extensively due to the abundance of existing materials, our focus will be on these rising stars that are making significant moves in the world of artificial intelligence. Each of these companies brings a unique perspective and range of capabilities, driving the development of LLMs and pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve.
1. Anthropic

Anthropic, founded in 2021 by former OpenAI employees, including the sibling duo Daniela and Dario Amodei, represents a new generation of AI development companies. With $1.5 billion in funding, the company has set out on a mission to create helpful, honest, and harmless AI systems.
Their flagship offering, Claude, is a highly advanced AI assistant that exemplifies the fruits of their research. Accessible through a chat interface and API, Claude is known for its extensive capabilities in conversational and text processing tasks, offering a high degree of reliability and predictability that sets it apart.
One of Claude’s remarkable features is its context length which, at 75,000 words (100K tokens), far surpasses that of its contemporaries like GPT-4. This allows Claude to digest and comprehend substantial amounts of text, such as an entire novel like ‘The Great Gatsby’, in mere seconds.
Claude has proven to be an adept tool in a variety of use cases including summarization, search, creative and collaborative writing, Q&A, coding, and more. Early adopters praise Claude’s enhanced safety measures, ease of conversation, and steerability, leading to more effective and efficient outputs. Adding to its versatility, Claude can also adapt to specific directions on personality, tone, and behavior.
There are currently two versions of Claude: the high-performance Claude and Claude Instant, which offers a lighter, faster, and less expensive alternative without compromising significantly on capabilities.
What truly distinguishes Claude is Anthropic’s novel technique called “constitutional AI”. This principle-based approach aims to align AI systems better with human intentions, providing a simple set of guiding principles for AI responses.
Claude’s impressive capabilities have garnered significant praise from users and clients. Quora users have noted its enhanced conversational and creative abilities, while Robin AI lauded its potential in legal contexts, like evaluating and suggesting alternative language in contracts. These testimonials highlight Claude’s potential to become a game-changer in the landscape of Large Language Models.
Anthropic’s success extends beyond its innovative offerings; it is perhaps best demonstrated by its integration with major platforms such as Quora, Slack, Notion, Zoom, and AssemblyAI. The integration of Claude, Anthropic’s flagship AI model, into these platforms represents a significant milestone in the field of AI applications.
Decoding Anthropic Model Variants and Pricing Models
Anthropic offers two primary variants of their flagship model, Claude, each optimized for distinct use-cases and offering unique advantages.
The first variant is Claude Instant. This model has been optimized for low latency and high throughput applications, making it ideal for scenarios where rapid response times are critical. Despite offering performance at 1/6th the cost of the standard Claude model, it retains a generous context window of 9,000 tokens, enabling it to understand and respond to complex inputs effectively. Claude Instant is priced at $0.43 per million characters for prompts and $1.45 per million characters for outputs, making it an affordable option for many developers. Additionally, dedicated capacity is available for Claude Instant, allowing for predictable performance even at scale, and it can be run on a device as common as a MacBook Pro.
The second variant is Claude-v1, the company’s best-in-class offering. This model is designed for superior performance, especially in tasks that require complex reasoning and extensive contextual understanding. Like Claude Instant, it too has a context window of 9,000 tokens. However, its pricing reflects its advanced capabilities, with prompts and outputs priced at $2.90 and $8.60 per million characters, respectively. Claude-v1 also supports dedicated capacity and can be run on a MacBook Pro.
In summary, whether you are seeking an AI solution for high-speed, high-throughput applications, or looking for an AI that excels in complex reasoning, Anthropic’s Claude model family provides options that can be tailored to your specific needs. The availability of dedicated capacity for both models further assures consistent performance, making Anthropic’s offerings adaptable to a broad range of applications.
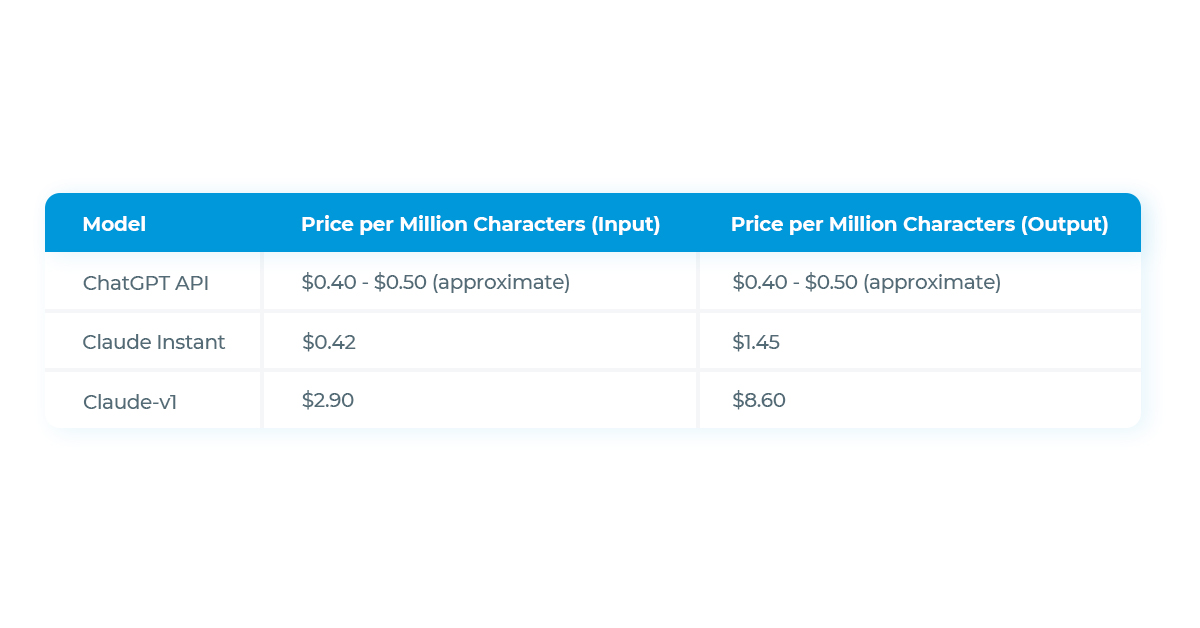
Indeed, when directly comparing the pricing models of Anthropic’s Claude Instant and Claude-v1 with OpenAI’s ChatGPT, it is clear that both of Anthropic’s offerings come at a higher price point.
Claude Instant, the more affordable variant from Anthropic, is priced slightly higher than ChatGPT for input and approximately three times higher for output per million characters. Claude-v1, the premium offering, is significantly more expensive than both ChatGPT and Claude Instant, with its output pricing exceeding that of ChatGPT by more than seventeen times.
This pricing strategy reflects Anthropic’s positioning of their LLMs as superior in terms of capabilities and features. While ChatGPT has been a popular and cost-effective choice for many developers and businesses, Anthropic is making a bold statement about the value and advanced features their models bring to the table.
While this means that Anthropic’s offerings may be out of reach for some budget-conscious projects, the company is clearly targeting use-cases where high-quality and complex reasoning abilities are paramount, and where customers are willing to invest more for these advanced features. Despite the higher price tag, the versatility, advanced capabilities, and unique features of Claude Instant and Claude-v1 demonstrate their value proposition in the rapidly evolving LLM landscape.
2. Cohere

Cohere, founded in 2019 by Aidan Gomez, Ivan Zhang, and Nick Frosst (an early member of Google’s Toronto AI lab), is carving out a unique niche in the vast LLM landscape. The company was created on a strong foundation, with Gomez being one of the co-authors of the game-changing paper “Attention Is All You Need,” which introduced the Transformer architecture, the backbone of successful LLMs such as OpenAI’s GPT-4.
Cohere has made significant strides in the AI industry, as evidenced by their $435M funding. Their signature large language model, Command, stands testament to their commitment to revolutionizing natural language processing technologies. The robust funding reflects investor confidence in their innovative approaches, particularly with Command, a powerful LLM designed to help businesses across a range of industries tackle complex text generation and analysis tasks.
The company offers an API that facilitates access to natural language processing and large language model technologies. Cohere’s platform is highly versatile, capable of generating or analyzing text to accomplish tasks such as content writing, moderation, data classification, and information extraction at an impressive scale. Customers can access the platform through its API, managed services, or popular cloud machine learning platforms like Amazon Sagemaker and Google Vertex AI.
Understanding the needs of enterprise customers with stringent data-protection and latency requirements, Cohere also offers private LLM deployments on VPC or even on-premises. This customer-focused approach is also evident in their development of multilingual language models trained on data from native speakers, showcasing their commitment to delivering practical solutions for diverse enterprise needs.
A key feature of Cohere’s AI platform is its cloud-agnostic nature. This means it can be deployed across various public clouds, including Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services, a customer’s existing cloud infrastructure, virtual private clouds, or even on-site. The company maintains a hands-on relationship with its customers, collaborating to create custom LLMs based on proprietary data.
Cohere’s vision transcends the conventional boundaries of text analysis and generation. They plan to build models that can perform tasks, such as scheduling meetings, booking flights, or filing expense reports, thereby transforming AI from a passive tool into an active assistant. The company’s primary focus is to empower customers to create proprietary LLM capabilities using their data, thereby creating strategic differentiation and business value.
Decoding Cohere Pricing Models
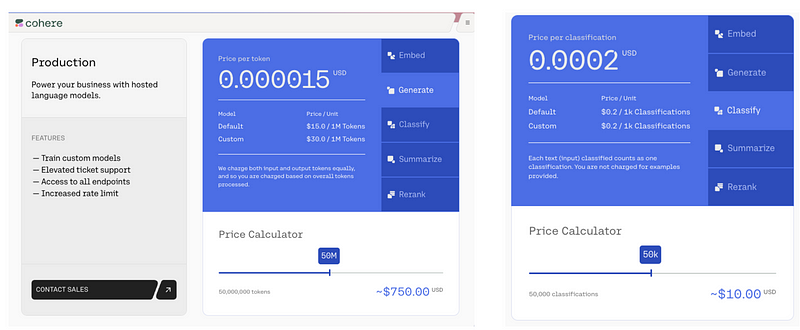
Pricing model for Cohere
When comparing Cohere’s pricing structure with Anthropic’s Claude and OpenAI’s ChatGPT, the first thing that stands out is the difference in the way these companies define their pricing models.
While Anthropic and OpenAI charge based on the number of characters input and output, Cohere’s pricing model is task-oriented. They charge $15 per million tokens for text generation, a task equivalent to the output pricing in Anthropic’s and OpenAI’s models. However, their pricing for classification tasks, another integral aspect of NLP applications, is separate and charged at $0.2 per 1,000 tasks. This allows for more flexibility, as customers can choose to pay for the tasks they specifically require.
In a direct comparison, Cohere’s pricing per million tokens for text generation is higher than both Anthropic’s Claude Instant and ChatGPT. The matrix below provides an insightful comparison of the performances of three leading large language models (LLMs): ChatGPT from OpenAI, Claude from Anthropic, and Command from Cohere. Each model has unique strengths and performances in various areas such as offensive language detection, email reply generation (content generation), mathematical problem generation and solving.
Skill Matrix: Comparative Analysis of Performance Across Key LLMs
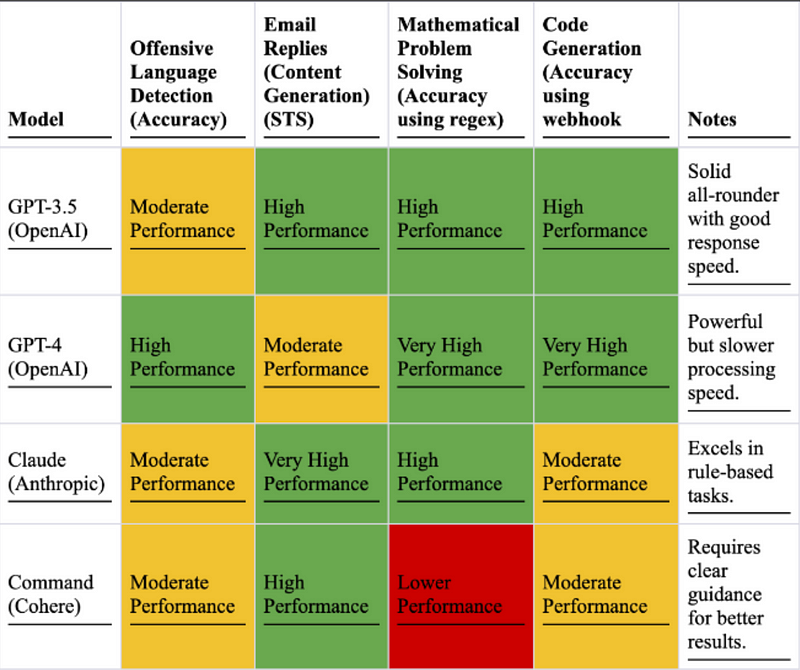
Comparative Analysis of Performance Across Key LLMs
ChatGPT, both the 3.5 and the GPT-4 versions, demonstrates solid overall performance, showing high capabilities in both offensive language detection and email reply generation. The GPT-3.5 iteration shows moderate performance in detecting offensive language while excelling in content generation for tasks like email replies. On the other hand, GPT-4 shows high performance in detecting offensive language but a moderate performance in email reply generation. Both versions are noted to be solid all-rounders, with GPT-4 having slower processing speed but more powerful capabilities.
Anthropic’s Claude, on the other hand, demonstrates a moderate performance in offensive language detection but shines in content generation with a very high performance in tasks like email replies. It also demonstrates very high performance in both mathematical problem generation and solving, especially when rule-based tasks are involved.
Finally, Cohere’s Command demonstrates a moderate performance in both offensive language detection and email reply generation. However, it shines in the field of mathematical problem generation and solving, showing very high performance. A note about Command is that it requires clear guidance for better results.
These comparisons reflect the diverse capabilities of different LLMs in the market and how they could cater to various needs and applications in different industries. It showcases the fact that no one model excels in all tasks, and the choice of model would largely depend on the specific use-cases an individual or a company might have.
3. Mosaic ML
(now acquired by Databricks in July 2023, at $1.3B)

The caliber of talent behind MosaicML is exceptional. CEO Naveen Rao, a seasoned entrepreneur and former founder and CEO of Nervana Systems, brings deep expertise in deep learning and ML platforms. His co-founders, CTO Hanlin Tang and Chief Science Officer Jonathan Frankle, further strengthen the team. Tang, a former Director of Intel AI Lab, has extensive experience in AI research and development. Frankle, known for his influential work on efficient deep learning, authored the renowned paper on the “Lottery Ticket Hypothesis”.
The recent launch of MPT-7B, part of MosaicML’s Foundation Series, sets a new standard for open-source, commercially usable large language models (LLMs). MPT-7B is a transformer model trained from scratch on 1 trillion tokens of text and code. It offers high-quality results and is available for commercial use, providing enterprises with a powerful and efficient solution for training and deploying LLMs.
The MPT model series distinguishes itself by addressing the challenges faced by enterprises in training and deploying open-source models. MosaicML’s MPT-7B, with its FlashAttention and #ALiBi features, ensures quick training and inference, along with finetuning and extrapolation capabilities. The model series also offers efficient open-source training code and is licensed under Apache-2.0.
To showcase the adaptability of the MPT model series, MosaicML has released three fine-tuned variations: MPT-7B-StoryWriter-65k+, MPT-7B-Instruct, and MPT-7B-Chat. These models demonstrate the potential of the MPT series in various contexts, such as generating long-contextualized stories, providing short-form instructions, and engaging in chatbot-like conversations.
The MPT-7B base model, along with the fine-tuned variants, has already gained significant popularity in the ML community, with over 3 million downloads since its launch. Community contributions include projects like LLaVA-MPT, which incorporates vision understanding into MPT, GGML, which optimizes MPT for Apple Silicon and CPUs, and GPT4All, enabling users to run GPT4-like chatbots on their laptops using MPT as a backend model.
Building on the success of MPT-7B, MosaicML has expanded its Foundation Series with the introduction of MPT-30B. This open-source model, licensed for commercial use, outperforms the original GPT-3 and offers exceptional power and performance. Fine-tuned variants, MPT-30B-Instruct and MPT-30B-Chat, excel in single-turn instruction following and multi-turn conversations, respectively.
With special features like an 8k token context window, support for longer contexts via ALiBi, and efficient inference and training performance through FlashAttention, MPT-30B provides enterprises with advanced capabilities for natural language processing tasks. MosaicML’s commitment to providing powerful models that can be deployed on a single GPU ensures cost-effectiveness and accessibility for enterprises of all sizes.
MosaicML’s success is fueled by its optimization of systems and algorithms, resource utilization, and packaging for user-friendliness. Their approach makes every computing dollar spent on training large ML models significantly more efficient and effective. The company has published the costs of training compute-optimal LLMs, demonstrating that achieving the same quality as the original GPT-3 can be achieved for less than $500K.
With this remarkable team and their innovative approach to ML model training, MosaicML is making significant strides in improving the efficiency and accessibility of AI technologies. Their commitment to driving advancements in the field positions them as a key player in the rapidly evolving landscape of large language models.
4. Cerebras

Founded in 2015, Cerebras has amassed $715M in funding and made significant waves in the AI landscape with its innovative Cerebras-GPT large language models. Demonstrating a commitment to the open-source community, Cerebras has recently open-sourced a suite of seven GPT models. The range of these models is quite impressive, boasting parameters from 111 million all the way up to a staggering 13 billion. The company has made these models readily available on popular platforms such as GitHub and Hugging Face.
The innovative capacity of Cerebras Systems becomes evident when looking at the extraordinary accomplishments they’ve achieved in the realm of AI hardware. In an industry first, Cerebras trained a series of seven GPT models on the Andromeda AI supercomputer. These models ranged in complexity from 111 million parameters up to an impressive 13 billion parameters. While such an endeavor would ordinarily take several months, Cerebras was able to complete the process in just a few weeks. This impressive speed was made possible by the powerful Cerebras CS-2 systems that compose the Andromeda supercomputer and the unique weight streaming architecture of Cerebras, which effectively eliminates the challenges of distributed compute.
This achievement underscores Cerebras’ capacity to handle the largest and most complex AI workloads currently in existence. Cerebras’ technology is notable not just for its capabilities but also for its efficiency. Despite the typically lengthy timeline for training these types of models, the speed of Cerebras’ CS-2 systems in Andromeda, paired with their unique weight streaming architecture, has cut this time down to just a few weeks. This level of efficiency extends to their personnel as well, with the company claiming to need just a single person to train all the models, a stark contrast to the team of 35 needed for GPT-4.
By drastically reducing training time for these large-scale models, Cerebras has shown that it’s possible to accelerate the development and deployment of LLMs without sacrificing their complexity or functionality. This represents a significant stride forward in the field of artificial intelligence, offering promising potential for the rapid advancement and adoption of these powerful models in various applications.
Further demonstrating the potential applications of their technology, Cerebras recently announced a partnership with Jasper AI, a leading AI content platform. The collaboration will harness the power of the Cerebras AI Model Studio, hosted on the Cirrascale AI Innovation Cloud. This platform allows users to train generative Transformer (GPT)-class models, including GPT-J, GPT-3, and GPT-NeoX, on Cerebras Wafer-Scale Clusters, including the recently announced Andromeda AI supercomputer.
Highlighting the advantages of their technology, Cerebras reports that training GPT-J on traditional cloud services from scratch takes approximately 64 days, but with the Cerebras AI Model Studio, this time can be significantly reduced to just eight days. Moreover, the financial savings are substantial: traditional cloud-based production costs on GPUs alone can reach up to $61,000, while Cerebras achieves a full production run for just $45,000. These numbers underscore Cerebras’ competitive edge in the LLM landscape in terms of both efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
5. Aleph Alpha

Based in Heidelberg, Germany, Aleph Alpha is a startup that was founded in 2019 by Jonas Andrulis and Samuel Weinbach. The company has created an AI chatbot called Lumi, which is built on a Large Language Model (LLM) known as Luminous. This model is touted as “Europe’s most sophisticated AI base technology for value creation.”
The primary aim of Aleph Alpha is to research, develop, and operationalize large AI systems with a focus on achieving generalizable AI. Their platform offers models similar to GPT-3 for tasks involving text, vision, and strategy. Furthermore, Aleph Alpha runs a public API that allows both the public and private sectors to run their own AI experiments, fostering the development of new business models.
Despite having raised only $31.1 million, compared to OpenAI’s staggering $11 billion, Aleph Alpha impresses in the realm of data. The company’s largest model is trained on an impressive 300 billion parameters, outperforming OpenAI’s model, which is trained on 175 billion parameters.
Aleph Alpha’s chatbot Lumi, constructed on the Luminous LLM, resembles OpenAI’s ChatGPT in many ways. However, the company sets itself apart by striving to become a “sovereign EU-based compute infrastructure” for Europe’s private and public sectors. This mission aligns them firmly within the realm of EU law, GDPR, and regulation, potentially making them a secure “Fortress Europe” within the industry.
Targeting “critical enterprises”, such as law firms, healthcare providers, and banks, Aleph Alpha caters to organizations that heavily rely on trustworthy, accurate information. By leveraging its AI technology, Aleph Alpha offers these industries the ability to access and utilize advanced AI models within a trusted and regulatory-compliant environment.
6. AI21 Labs

AI21 Labs, founded in 2017, has emerged as a leading player in the field of AI, spearheaded by a team of AI pioneers and technology veterans. The founding members include Professor Yoav Shoham, an esteemed Professor Emeritus at Stanford, Ori Goshen, the Founder of CrowdX, and Professor Amnon Shashua, the Founder of Mobileye, who serves as the chairman.
AI21 Labs’ flagship offering is the Jurassic-2 large language model (LLM), which boasts an impressive 178 billion parameters. The company’s AI21 Studio provides API access to the Jurassic-2 model, empowering developers to leverage its advanced text generation and comprehension capabilities in thousands of live applications. Additionally, AI21 Labs has made significant advancements in enhancing LLMs with discrete reasoning experts through their modular reasoning knowledge and language system, known as the MRKL system (pronounced “miracle”). This system integrates tools like online calculators and currency converters to augment the language models. The first implementation of this system, Jurassic-X, incorporates language models enriched with weather apps and Wikidata.
The Jurassic-2 LLM is accessible to developers through APIs for implementation, and it is an integral part of AI21’s suite of products, including the Wordtune suite of services. Wordtune, a browser extension developed by AI21 Labs, has gained recognition as one of Google’s favorite extensions for 2021. It offers a range of powerful features that assist users in refining and improving their written content. AI21 Labs has also introduced Wordtune Read, a tool that utilizes advanced analysis and summarization techniques to enable users to quickly and efficiently read and comprehend long and complex texts.
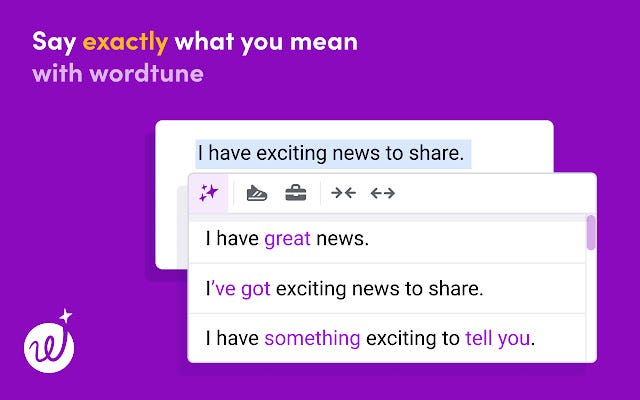
Wordtune is an AI powered reading and writing companion capable of fixing grammatical errors, understanding context and meaning, suggesting paraphrases or alternative writing tones, and generating written text based on context. It is developed by an Israeli AI company AI21 Labs (source: official website).
AI21 Labs is continuously pushing the boundaries of AI language models. Their work on “in-context retrieval augmented language modeling” focuses on training language models to retrieve information from external sources, allowing them to identify the most relevant documents in response to a given prompt. This development showcases the company’s dedication to improving the contextual understanding and information retrieval capabilities of their LLMs.
With a strong focus on cutting-edge AI research and practical applications, AI21 Labs has positioned itself as a key player in the field, offering innovative solutions that enhance language comprehension, generation, and reasoning.
7. John Snow Labs

John Snow Labs, an award-winning healthcare NLP company, is making waves in the field by rebranding itself as a Healthcare LLM company. With its renowned Spark NLP, Healthcare NLP, Visual NLP, and LangTest libraries, downloaded over 60 million times worldwide, John Snow Labs is becoming a prominent contender in the world of large language models (LLMs).
The company’s latest release, BioGPT-JSL, is specifically tailored to the medical domain, enabling a range of common healthcare use cases. From medical Q&A and interpreting research articles to generating clinical text and summarizing patient encounters, BioGPT-JSL demonstrates exceptional accuracy and domain-specific expertise.
Compared to general-purpose LLMs, John Snow Labs’ healthcare-specific models deliver superior performance. Clinical note summarization, clinical entity recognition, de-identification, and ICD-10-CM code extraction achieve significantly higher accuracy rates than models like ChatGPT and GPT-4. These benchmarks are publicly available, showcasing the robustness and reliability of John Snow Labs’ offerings. Read more about these benchmarks and the story behind them here.
What sets John Snow Labs apart is its commitment to production readiness. Designed for high-compliance industries like healthcare, their models operate on users’ infrastructure, ensuring privacy and security. They are engineered to run on commodity hardware, enabling faster and more cost-effective scaling. Regular updates keep the models aligned with the latest research papers, clinical trials, guidelines, and terminologies, ensuring they remain up to date for production applications.
John Snow Labs’ healthcare-specific language models are part of their comprehensive Healthcare NLP suite, empowering data scientists with Python libraries, models, and notebooks. Users gain access to regularly refreshed models and all new releases, guaranteeing access to the latest advancements. The company’s agility is key as the field evolves rapidly, requiring rebuilding and fine-tuning models to stay at the forefront of healthcare NLP.
With its expertise, focus on healthcare-specific challenges, and dedication to production-ready solutions, John Snow Labs is emerging as a formidable player in the realm of large language models, offering transformative capabilities for healthcare organizations and researchers.
Compliance Check: Do Foundation Model Providers Abide by the Draft EU AI Act?
A recent study conducted by researchers from Stanford University has raised concerns that the world’s leading ten AI language models may not meet the stringent standards outlined in the European Union’s upcoming AI Act. The AI Act, which is set to become the first comprehensive set of regulations for AI, could have significant implications for AI practices globally, with potential heavy fines for non-compliant AI systems.
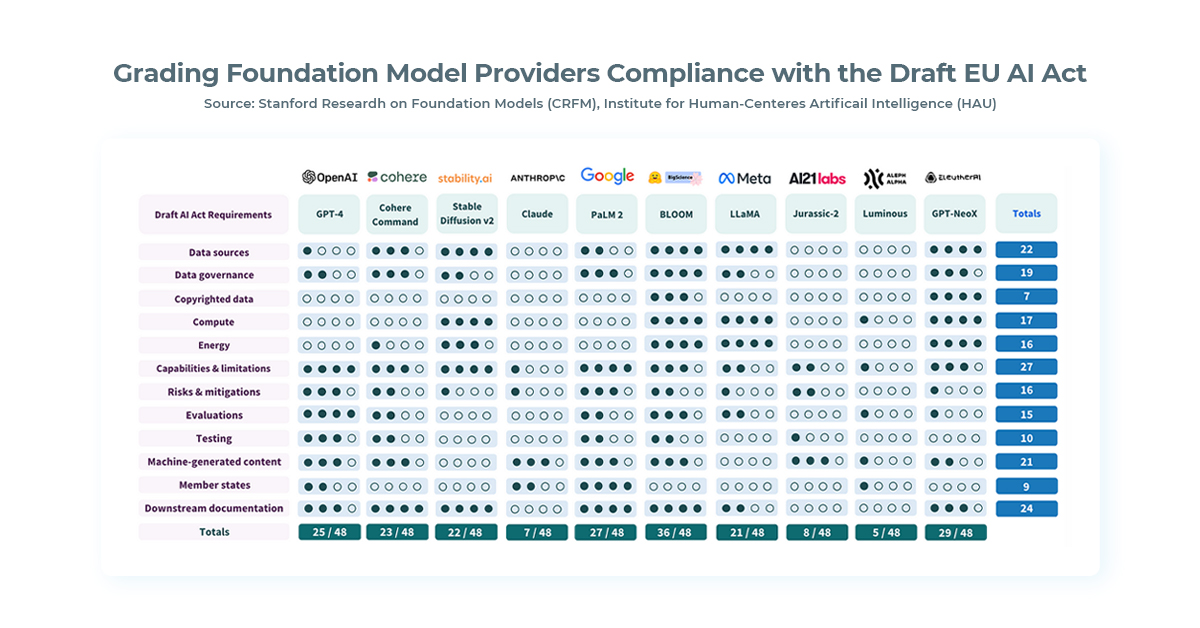
Model compliance against 12 key requirements in the EU’s AI Act (source: Stanford HAI)
The EU’s AI Act, recently approved in a parliamentary vote, is expected to impact more than 450 million individuals and serve as a blueprint for other nations in crafting their own AI regulations. While recent clarifications exempt foundation models like GPT-4 from the “high-risk” AI category, generative AI models are still subject to various requirements under the AI Act, including registration with authorities and transparency disclosures.
Non-compliance with the AI Act could result in fines of up to €20M or 4% of a company’s worldwide revenue. This poses significant challenges for AI language models, particularly in meeting the Act’s compliance requirements, where many models currently fall short. The study evaluated ten leading AI models against the draft AI Act’s compliance requirements and found that most models scored below 50% in overall compliance.
Notably, closed-source models like OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Google’s PaLM 2 received low scores, while open-source models like Hugging Face’s BLOOM performed relatively better. However, the study identified areas of uncertainty, such as the dimensions of performance required for compliance and the enforcement mechanisms for the AI Act.
Despite these challenges, the researchers highlight the importance of implementing the AI Act. They believe that it can serve as a catalyst for AI creators to establish industry standards, enhance transparency, and bring about positive changes in the foundation model ecosystem. As the AI landscape continues to evolve, navigating compliance with regulatory frameworks like the EU AI Act will be crucial for AI language models and their creators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the landscape of large language model (LLM) companies is rich and diverse, with each player bringing its unique offerings and contributions to the field of artificial intelligence. Companies like Anthropic, Cohere, Cerebras, Aleph Alpha, and AI21 Labs have demonstrated their commitment to advancing AI technologies and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Anthropic stands out with its focus on developing AI systems that align with human intentions, leveraging techniques like “constitutional AI” to guide their models’ responses. Cohere excels in providing AI solutions for enterprise use cases, offering powerful tools for text generation, analysis, and mathematical problem-solving. Cerebras impresses with its open-sourcing initiatives and the ability to train large-scale models with remarkable efficiency and speed. Aleph Alpha aims to be a trusted EU-based compute infrastructure, catering to critical enterprises with their LLM capabilities. AI21 Labs showcases its expertise in language models, offering API access to its Jurassic-2 model and innovative products like Wordtune.
As the AI landscape continues to evolve, these companies are shaping the future of AI development and applications. Their contributions not only enhance language processing and generation but also drive progress in areas such as natural language understanding, reasoning, and context retrieval. With their diverse approaches, funding, and partnerships, these LLM companies are transforming industries, revolutionizing business models, and paving the way for a more intelligent and interconnected world.
The landscape of LLM companies is vibrant and dynamic, and the advancements made by these leading players are pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve. As we look to the future, it is clear that LLMs will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping various industries, enabling new possibilities, and driving innovation across the board. The race to develop more sophisticated, ethical, and powerful LLMs is ongoing, and we can expect further breakthroughs that will redefine the way we interact with AI systems and leverage their capabilities.






























